New Recombinant Antimicrobial Peptides Confer Resistance to Fungal Pathogens in Tobacco Plants
- PMID: 32903611
- PMCID: PMC7438598
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01236
New Recombinant Antimicrobial Peptides Confer Resistance to Fungal Pathogens in Tobacco Plants
Abstract
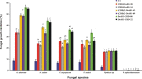
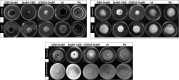
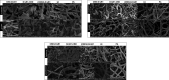
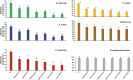
Antimicrobial peptides have been long known to confer resistance to plant pathogens. In this study, new recombinant peptides constructed from a dermaseptin B1 (DrsB1) peptide fused to a chitin-binding domain (CBD) from Avr4 protein, were used for Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of tobacco plants. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR), semi-quantitative RT-PCR, and western blotting analysis demonstrated the incorporation and expression of transgenes in tobacco genome and transgenic plants, respectively. In vitro experiments with recombinant peptides extracted from transgenic plants demonstrated a significant (P<0.01) inhibitory effect on the growth and development of plant pathogens. The DrsB1-CBD recombinant peptide had the highest antifungal activity against fungal pathogens. The expression of the recombinant peptides greatly protected transgenic plants from Alternaria alternata, Alternaria solani, Fusarium oxysporum, and Fusarium solani fungi, in comparison to Pythium sp. and Pythium aphanidermatum. Expression of new recombinant peptides resulted in a delay in the colonization of fungi and appearance of fungal disease symptoms from 6 days to more than 7 weeks. Scanning electron microscopy images revealed that the structure of the fungal mycelia appeared segmented, cling together, and crushed following the antimicrobial activity of the recombinant peptides. Greenhouse bioassay analysis showed that transgenic plants were more resistant to Fusarium and Pythium infections as compared with the control plants. Due to the high antimicrobial activity of the recombinant peptides against plant pathogens and novelty of recombinant peptides, this report shows the feasibility of this approach to generate disease resistance transgenic plants.
Keywords: antifungal; chitin-binding domain; effector protein; expression; genetic engineering; transgenic plant.
Copyright © 2020 Khademi, Varasteh-Shams, Nazarian-Firouzabadi and Ismaili.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Targeting microbial pathogens by expression of new recombinant dermaseptin peptides in tobacco.Microbiologyopen. 2019 Nov;8(11):e837. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.837. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Microbiologyopen. 2019. PMID: 30912302 Free PMC article.
-
Production of a Recombinant Dermaseptin Peptide in Nicotiana tabacum Hairy Roots with Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity.Mol Biotechnol. 2019 Apr;61(4):241-252. doi: 10.1007/s12033-019-00153-x. Mol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30649664
-
Fusion of a chitin-binding domain to an antibacterial peptide to enhance resistance to Fusarium solani in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum).3 Biotech. 2018 Sep;8(9):391. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1416-7. Epub 2018 Aug 28. 3 Biotech. 2018. PMID: 30175028 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of pathogen-induced expression and efficacy of two amphibian antimicrobial peptides, MsrA2 and temporin A, for engineering wide-spectrum disease resistance in tobacco.Plant Biotechnol J. 2007 Nov;5(6):720-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2007.00277.x. Epub 2007 Jul 21. Plant Biotechnol J. 2007. PMID: 17645440
-
Lactoferrin-derived resistance against plant pathogens in transgenic plants.J Agric Food Chem. 2013 Dec 4;61(48):11730-5. doi: 10.1021/jf400756t. Epub 2013 Aug 9. J Agric Food Chem. 2013. PMID: 23889215 Review.
Cited by
-
Heterologous Production of Antimicrobial Peptides: Notes to Consider.Protein J. 2024 Apr;43(2):129-158. doi: 10.1007/s10930-023-10174-w. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Protein J. 2024. PMID: 38180586
-
Expression of a novel NaD1 recombinant antimicrobial peptide enhances antifungal and insecticidal activities.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 5;14(1):23235. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73710-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39369025 Free PMC article.
-
Co-expression of four penaeidins in transgenic rice seeds: an alternative strategy for substitute antibiotic agricultural products.Transgenic Res. 2023 Oct;32(5):463-473. doi: 10.1007/s11248-023-00361-x. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Transgenic Res. 2023. PMID: 37535257
-
Antimicrobial Peptides: Classification, Mechanism, and Application in Plant Disease Resistance.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Jun;17(3):1432-1446. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10478-6. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 39969681 Review.
-
Fabrication and Characterization of Buforin I-Loaded Electrospun Chitosan/Polyethylene Oxide Nanofibrous Membranes with Antimicrobial Activity for Food Packing Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Feb 19;17(4):549. doi: 10.3390/polym17040549. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chakraborty S., Newton A. C. (2011). Climate change, plant diseases and food security: an overview. Plant Pathol. 60 (1), 2–14. 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2010.02411.x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

