Blood-Brain Barrier: More Contributor to Disruption of Central Nervous System Homeostasis Than Victim in Neurological Disorders
- PMID: 32903669
- PMCID: PMC7438939
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00764
Blood-Brain Barrier: More Contributor to Disruption of Central Nervous System Homeostasis Than Victim in Neurological Disorders
Abstract
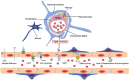
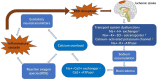
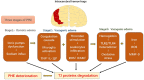
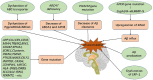
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a dynamic but solid shield in the cerebral microvascular system. It plays a pivotal role in maintaining central nervous system (CNS) homeostasis by regulating the exchange of materials between the circulation and the brain and protects the neural tissue from neurotoxic components as well as pathogens. Here, we discuss the development of the BBB in physiological conditions and then focus on the role of the BBB in cerebrovascular disease, including acute ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage, and neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), and multiple sclerosis (MS). Finally, we summarize recent advancements in the development of therapies targeting the BBB and outline future directions and outstanding questions in the field. We propose that BBB dysfunction not only results from, but is causal in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders; the BBB is more a contributor to the disruption of CNS homeostasis than a victim in neurological disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; acute ischemic stroke; blood-brain barrier; intracerebral hemorrhage; multiple sclerosis.
Copyright © 2020 Xiao, Xiao, Yang, Lan and Fang.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanistic Insights, Treatment Paradigms, and Clinical Progress in Neurological Disorders: Current and Future Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 10;24(2):1340. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021340. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Therapeutic Benefits of Intravenously Administrated Nanoparticles in Stroke and Age-related Neurodegenerative Diseases.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(24):1985-2000. doi: 10.2174/1381612828666220608093639. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 35676838
-
Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs): An Advanced Drug Delivery System Targeting Brain through BBB.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 31;13(8):1183. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081183. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revealing the mechanisms of blood-brain barrier in chronic neurodegenerative disease: an opportunity for therapeutic intervention.Rev Neurosci. 2024 Jul 8;35(8):895-916. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2024-0040. Print 2024 Dec 17. Rev Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38967133 Review.
-
Astrocytic modulation of blood brain barrier: perspectives on Parkinson's disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Aug 4;8:211. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00211. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25136294 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Psychobiotic Properties of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 31;25(17):9489. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179489. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitigation of avermectin exposure-induced brain tissue damage in carp by quercetin.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2023 Dec;49(6):1171-1185. doi: 10.1007/s10695-023-01249-7. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37831371
-
Nutritional Supplementation of Naturally Occurring Vitamin D to Improve Hemorrhagic Stroke Outcomes.Front Neurol. 2021 Jul 30;12:670245. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.670245. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34393969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Addressing Blood-Brain Barrier Impairment in Alzheimer's Disease.Biomedicines. 2022 Mar 22;10(4):742. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040742. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of non-classical NMDA receptors by glycine impairs barrier function of brain endothelial cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Aug 11;79(9):479. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04502-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35951110 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

