Sortase A Mediated Bioconjugation of Common Epitopes Decreases Biofilm Formation in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 32903711
- PMCID: PMC7438799
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01702
Sortase A Mediated Bioconjugation of Common Epitopes Decreases Biofilm Formation in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
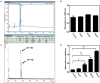
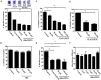
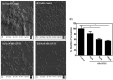
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most notorious pathogens and is frequently associated with nosocomial infections imposing serious risk to immune-compromised patients. This is in part due to its ability to colonize at the surface of indwelling medical devices and biofilm formation. Combating the biofilm formation with antibiotics has its own challenges like higher values of minimum inhibitory concentrations. Here, we describe a new approach to target biofilm formation by Gram positive bacteria. Sortase A is a transpeptidase enzyme which is responsible for tagging of around ∼22 cell surface proteins onto the outer surface. These proteins play a major role in the bacterial virulence. Sortase A recognizes its substrate through LPXTG motif. Here, we use this approach to install the synthetic peptide substrates onS. aureus. Sortase A substrate mimic, 6His-LPETG peptide was synthesized using solid phase peptide chemistry. Incorporation of the peptide on the cell surface was measured using ELISA. Effect of peptide incubation on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm was also studied. 71.1% biofilm inhibition was observed with 100 μM peptide while on silicon coated rubber latex catheter, 45.82% inhibition was observed. The present work demonstrates the inability of surface modified S. aureus to establish biofilm formation thereby presenting a novel method for attenuating its virulence.
Keywords: LPXTG; S. aureus; Sortase A; biofilm; infection.
Copyright © 2020 Kumari, Nath, Murty, Ravichandiran and Mohan.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthetic LPETG-containing peptide incorporation in the Staphylococcus aureus cell-wall in a sortase A- and growth phase-dependent manner.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 19;9(2):e89260. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089260. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586638 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of Staphylococcus aureus sortase A and its substrate complex.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 23;279(30):31383-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401374200. Epub 2004 Apr 26. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15117963
-
Substrate-derived Sortase A inhibitors: targeting an essential virulence factor of Gram-positive pathogenic bacteria.Chem Sci. 2023 May 31;14(25):6975-6985. doi: 10.1039/d3sc01209c. eCollection 2023 Jun 28. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 37389257 Free PMC article.
-
Sortase-catalysed anchoring of surface proteins to the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus.Mol Microbiol. 2001 Jun;40(5):1049-57. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02411.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11401711 Review.
-
Methicillin resistance and the biofilm phenotype in Staphylococcus aureus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Jan 28;5:1. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00001. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25674541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Transpeptidase Sortase A Binds Nucleic Acids and Mediates Mammalian Cell Labeling.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jun;11(21):e2305605. doi: 10.1002/advs.202305605. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38581131 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Staphylococcal Cell-Wall Biosynthesis Protein FemX Through Steered Molecular Dynamics and Drug-Repurposing Approach.ACS Omega. 2023 Aug 2;8(32):29292-29301. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02691. eCollection 2023 Aug 15. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37599983 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of MA01 rhamnolipid on cell viability and expression of quorum-sensing (QS) genes involved in biofilm formation by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 1;12(1):14833. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19103-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36050412 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of kaffir lime essential oils and their active constituents against Staphylococcus aureus focusing on sortase A.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 18;11(2):e41977. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41977. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40013263 Free PMC article.
-
The Glycoprotein 340's Scavenger Receptor Cysteine-Rich Domain Promotes Adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Contact Lens Polymers.Infect Immun. 2022 Jan 25;90(1):e0033921. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00339-21. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Infect Immun. 2022. PMID: 34662210 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

