Integrative Analysis Revealing Human Heart-Specific Genes and Consolidating Heart-Related Phenotypes
- PMID: 32903789
- PMCID: PMC7438927
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00777
Integrative Analysis Revealing Human Heart-Specific Genes and Consolidating Heart-Related Phenotypes
Abstract
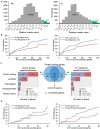
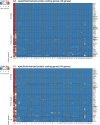
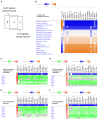
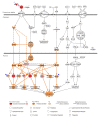
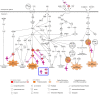
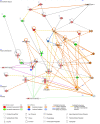
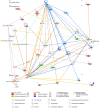
Elucidating expression patterns of heart-specific genes is crucial for understanding developmental, physiological, and pathological processes of the heart. The aim of the present study is to identify functionally and pathologically important heart-specific genes by performing the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA). Through a median-based analysis of tissue-specific gene expression based on the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) data, we identified 56 genes with heart-specific or elevated expressions in the heart (heart-specific/enhanced), among which three common heart-specific/enhanced genes and four atrial appendage-specific/enhanced genes were unreported regarding the heart. Differential expression analysis further revealed 225 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between atrial appendage and left ventricle. Our integrative analyses of those heart-specific/enhanced genes and DEGs with IPA revealed enriched heart-related traits and diseases, consolidating evidence of relationships between these genes and heart function. Our reports on comprehensive identification of heart-specific/enhanced genes and DEGs and their relation to pathways associated with heart-related traits and diseases provided molecular insights into essential regulators of cardiac physiology and pathophysiology and potential new therapeutic targets for heart diseases.
Keywords: differentially expressed genes; gene expression; heart disease; heart-specific genes; ingenuity pathway analysis.
Copyright © 2020 Ahn, Wu and Lee.
Figures


References
-
- Benjamini A., Hochberg Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B Stat. Methodol. 57 289–300. 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

