Long Noncoding RNA H19 Induces Neuropathic Pain by Upregulating Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 5-Mediated Phosphorylation of cAMP Response Element Binding Protein
- PMID: 32903807
- PMCID: PMC7445513
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S240273
Long Noncoding RNA H19 Induces Neuropathic Pain by Upregulating Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 5-Mediated Phosphorylation of cAMP Response Element Binding Protein
Retraction in
-
Long Noncoding RNA H19 Induces Neuropathic Pain by Upregulating Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 5-Mediated Phosphorylation of cAMP Response Element Binding Protein [Retraction].J Pain Res. 2021 Jul 30;14:2335. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S331373. eCollection 2021. J Pain Res. 2021. PMID: 34354372 Free PMC article.
Abstract
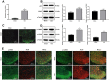
Objective: Neuropathic pain (NP) is a debilitating condition caused by nervous system injury and chronic diseases. LncRNA H19 is upregulated in many human diseases, including NP. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) aggressively worsens inflammatory action and nerve damage to cause severe NP. Phosphorylated cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) is detrimental to nerves and promotes NP progression. Herein, aim of our study was to assess the mechanism of lncRNA H19.
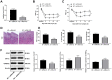
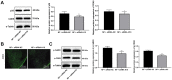
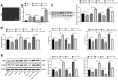
Methods: The NP rat model was established using chronic constriction injury (CCI). Paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) tests and paw withdrawal latency (PWL) tests were performed. Then, small interfering (si)RNA against H19 was intrathecally injected into rats to suppress H19 expression. Schwann cells were isolated from NP rats and transfected with siRNA-H19 or a lentivirus (LV)-based vector expressing H19. Inflammatory factors and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) were detected. Western blot analysis was conducted to detect CDK5/p35 and p-CREB expression. Finally, H19, CDK5 and CREB phosphorylation were tested with the combination of the CDK5 inhibitor roscovitine and transfection of LV-H19 and siRNA-H19. Finally, we investigated the binding relationships between H19 and miR-196a-5p and between miR-196a-5p and CDK5 and detected the mRNA expression of miR-196a-5p and CDK5 in rats with H19 knockdown and in Schwann cells with H19 knockdown.
Results: Highly expressed H19, CDK5/p-35 and p-CREB were observed in NP rats, accompanied by obviously decreased PWT and PWL, upregulated inflammatory factors and GFAP levels, and reduced 5-HT2A and GABAB2 expression. siRNA-H19 restored NP-related indexes and downregulated CDK5/p35 and p-CREB phosphorylation. siRNA-H19, together with the CDK5 inhibitor roscovitine, reduced CDK5 and p-CREB expression in Schwann cells isolated from NP rats. Binding sites between H19 and miR-196a-5p and between miR-196a-5p and CDK5 were identified. Silencing H19 upregulated miR-196a-5p expression and downregulated CDK5 levels.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that silencing H19 inhibited NP by suppressing CDK5/p35 and p-CREB phosphorylation via the miR-196a-5p/CDK5 axis, which may provide new insight into NP treatment.
Keywords: cAMP response element binding protein phosphorylation; cyclin-dependent kinases 5; long noncoding RNA H19; neuropathic pain; roscovitine.
© 2020 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biosynthesis inhibition of miR-142-5p in a N6-methyladenosine-dependent manner induces neuropathic pain through CDK5/TRPV1 signaling.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jan 31;30(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00695-w. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 39891095 Free PMC article.
-
The Long Noncoding RNA-H19 Mediates the Progression of Fibrosis from Acute Kidney Injury to Chronic Kidney Disease by Regulating the miR-196a/Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.Nephron. 2022;146(2):209-219. doi: 10.1159/000518756. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Nephron. 2022. PMID: 34818249
-
LncRNA H19 modulates neuropathic pain through miR-141/GLI2 axis in chronic constriction injury (CCI) rats.Transpl Immunol. 2022 Apr;71:101526. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2021.101526. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Transpl Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34999183
-
LncRNA PCAT19 Regulates Neuropathic Pain via Regulation of miR-182-5p/JMJD1A in a Rat Model of Chronic Constriction Injury.Neuroimmunomodulation. 2022;29(2):161-170. doi: 10.1159/000518847. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2022. PMID: 34518490
-
Cellular and Molecular Machinery of Neuropathic Pain: an Emerging Insight.Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2022;8(4):227-235. doi: 10.1007/s40495-022-00294-9. Epub 2022 May 23. Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35646513 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Long Non-coding RNAs in the Development of Chronic Pain.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Nov 23;14:760964. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.760964. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34887726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs and Their Role in Rodent Neuropathic Pain Models.J Pain Res. 2021 Dec 30;14:3935-3950. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S344339. eCollection 2021. J Pain Res. 2021. PMID: 35002313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Cdk5 in neurological disorders.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jul 28;16:951202. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.951202. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35966199 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

