Cofilin-1 Is a Mechanosensitive Regulator of Transcription
- PMID: 32903827
- PMCID: PMC7438942
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00678
Cofilin-1 Is a Mechanosensitive Regulator of Transcription
Abstract
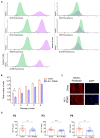
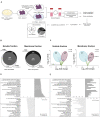
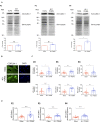
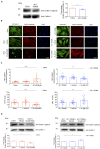
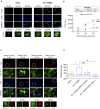
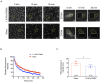
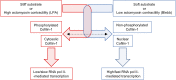
The mechanical properties of the extracellular environment are interrogated by cells and integrated through mechanotransduction. Many cellular processes depend on actomyosin-dependent contractility, which is influenced by the microenvironment's stiffness. Here, we explored the influence of substrate stiffness on the proteome of proliferating undifferentiated human umbilical cord-matrix mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. The relative abundance of several proteins changed significantly by expanding cells on soft (∼3 kPa) or stiff substrates (GPa). Many such proteins are associated with the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, a major player of mechanotransduction and cell physiology in response to mechanical cues. Specifically, Cofilin-1 levels were elevated in cells cultured on soft comparing with stiff substrates. Furthermore, Cofilin-1 was de-phosphorylated (active) and present in the nuclei of cells kept on soft substrates, in contrast with phosphorylated (inactive) and widespread distribution in cells on stiff. Soft substrates promoted Cofilin-1-dependent increased RNA transcription and faster RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription elongation. Cofilin-1 is part of a novel mechanism linking mechanotransduction and transcription.
Keywords: Cofilin-1; cytoskeleton; hUCM-MSCs; mechanotransduction; proteomics; transcription.
Copyright © 2020 Domingues, Geraldo, Anjo, Matos, Almeida, Caramelo, Lopes-da-Silva, Paiva, Carvalho, Pires das Neves, Manadas and Grãos.
Figures
References
-
- Anjo S. I., Santa C., Saraiva S. C., Freitas K., Barah F., Carreira B., et al. (2017). “Neuroproteomics using short GeLC-SWATH: from the evaluation of proteome changes to the clarification of protein function,” in Current Proteomic Approaches Applied to Brain Function, eds Santamaría E., Fernández-Irigoyen J. (Cham: Springer; ), 107–138. 10.1007/978-1-4939-7119-0_8 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

