Two Cases of Intrafamilial Transmission of Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Producing Both PVL and TSST-1 Causing Fatal Necrotizing Pneumonia and Sepsis
- PMID: 32903848
- PMCID: PMC7445494
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S262123
Two Cases of Intrafamilial Transmission of Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Producing Both PVL and TSST-1 Causing Fatal Necrotizing Pneumonia and Sepsis
Abstract
Introduction: Staphylococcus aureus produces numerous toxins, such as toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1) and Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL). We isolated community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) strains producing both TSST-1 and PVL isolated from severe necrotizing pneumonia cases in a Nepali family. Detection of these CA-MRSA strains is rare in the world, and infection with these strains can take a rapidly progressive and lethal course. In this study, we traced the clinical course of this case and conducted a genetic analysis of the isolated strains.
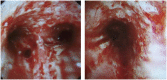
Case report: We described 2 familial cases (a 20-year-old male and 61-year-old female) of severe necrotizing pneumonia caused by CA-MRSA with the TSST-1 and PVL genes. A 20-year-old Nepalese male was admitted to our hospital after a 3-day history of high fever and coughing. Despite resuscitation efforts, he died of multiple organ failure. A 61-year-old Nepalese female was admitted to our hospital with a complaint of high fever and dyspnea for 1 day. She was the grandmother of the male subject and mostly stayed at his residence in Japan. We administered intravenous antibiotics, including anti-MRSA antibiotics, and she improved in 2 weeks. The sequence type of the isolates was ST22/SCCmec type IVa, and the spa type was t005. The virulence genes detected were as follows: PVL gene (lukSF-pv), TSST-1 gene (tst-1), sec, seg, sei, sel, sem, sen, seo, and seu. ST22 was not the dominant CA-MRSA clone type in Japan. Some of the reports demonstrated that PVL-/TSST-1-positive ST22-MRSA strains are prevalent in Nepal. Therefore, the MRSA strains were thought to be acquired from Nepal.
Conclusion: These cases highlight the emergence of TSST-1- and PVL-positive CA-MRSA infection and its association with life-threatening community-acquired necrotizing pneumonia. Clinicians should note the possibility of introducing MRSA strains from abroad and be aware of this illness to initiate appropriate treatment.
Keywords: CA-MRSA; PVL; Panton–Valentine leukocidin; TSST-1; community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; necrotizing pneumonia; toxic shock syndrome toxin 1.
© 2020 Hayakawa et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evolutionary dynamics of the novel ST22-PT methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clone co-harbouring Panton-Valentine leucocidin and duplicated toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 genes.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2024 Jun;30(6):779-786. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2024.02.020. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2024. PMID: 38408643
-
Community-acquired necrotizing pneumonia caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus producing Panton-Valentine leukocidin in a Chinese teenager: case report and literature review.Int J Infect Dis. 2014 Sep;26:17-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.02.025. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Int J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24980464 Review.
-
The emerging threat of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) clone ST22-PT, carrying both Panton-Valentine leucocidin and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 genes.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2023 Apr 3;78(4):1023-1027. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkad039. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2023. PMID: 36814074
-
Characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from bovine mastitis milk in South Korea: molecular characteristics, biofilm, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 22;12(12):e0119724. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01197-24. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39436122 Free PMC article.
-
Acute haematogenous community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis in an adult: case report and review of literature.BMC Infect Dis. 2012 Oct 25;12:270. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-270. BMC Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 23098162 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pneumonia Caused by Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Positive for Exfoliative Toxin A and Secondary to Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis.Cureus. 2022 May 25;14(5):e25334. doi: 10.7759/cureus.25334. eCollection 2022 May. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35774683 Free PMC article.
-
Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (TSST-1) in Staphylococcus aureus: Prevalence, Molecular Mechanisms, and Public Health Implications.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Jun 24;17(7):323. doi: 10.3390/toxins17070323. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40711134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Genomic Analysis of a Panton-Valentine Leukocidin-Positive ST22 Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Pakistan.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Apr 8;11(4):496. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11040496. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453247 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the Genotypic Characteristics of Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Collected in 244 Medical Facilities in Japan between 2010 and 2018: a Nationwide Surveillance.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0227221. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02272-21. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35758725 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular typing and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from burn wound infections in Fujian, China.Front Microbiol. 2023 Sep 20;14:1236497. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1236497. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37799609 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

