Diabetic Kidney Disease: Challenges, Advances, and Opportunities
- PMID: 32903946
- PMCID: PMC7445658
- DOI: 10.1159/000506634
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Challenges, Advances, and Opportunities
Abstract
Background: Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is the most common cause of the end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Regardless of intensive treatments with hyperglycemic control, blood pressure control, and the use of renin-angiotensin system blockades, the prevalence of DKD remains high. Recent studies suggest that the spectrum of DKD has been changed and many progresses have been made to develop new treatments for DKD. Therefore, it is time to perform a systemic review on the new developments in the field of DKD.
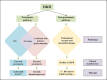
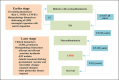
Summary: Although the classic clinical presentation of DKD is characterized by a slow progression from microalbuminuria to macroalbuminuria and by a hyperfiltration at the early stage and progressive decline of renal function at the late stage, recent epidemiological studies suggest that DKD patients have a variety of clinical presentations and progression rates to ESRD. Some DKD patients have a decline in renal function without albuminuria but display prominent vascular and interstitial fibrosis on renal histology. DKD patients are more susceptible to acute kidney injury, which might contribute to the interstitial fibrosis. A large portion of type 2 diabetic patients with albuminuria could have overlapping nondiabetic glomerular disease, and therefore, kidney biopsy is required for differential diagnosis for these patients. Only a small portion of DKD patients eventually progress to end-stage renal failure. However, we do not have sensitive and specific biomarkers to identify these high-risk patients. Genetic factors that have a strong association with DKD progression have not been identified yet. A combination of circulating tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)1, TNFR2, and kidney injury molecular 1 provides predictive value for DKD progression. Artificial intelligence could enhance the predictive values for DKD progression by combining the clinical parameters and biological markers. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors should be added to the new standard care of DKD patients. Several promising new drugs are in clinical trials.
Key messages: Over last years, our understanding of DKD has been much improved and new treatments to halt the progression of DKD are coming. However, better diagnostic tools, predictive markers, and treatment options are still urgently needed to help us to better manage these patients with this detrimental disease.
Keywords: Diabetic kidney disease; Inflammation; Nonproteinuric pathway; Progression; Treatment.
Copyright © 2020 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Karger Publishers [Internet] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: National Diabetes Statistics Report. 2017. [cited 2018 Feb 24]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics/statistics-report.html.
-
- Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018 Feb;14((2)):88–98. - PubMed
-
- Valencia WM, Florez H. How to prevent the microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes beyond glucose control. BMJ. 2017 Jan;356:i6505. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

