Histological investigation of picosecond laser-toning and fractional laser therapy
- PMID: 32904059
- PMCID: PMC7447825
- DOI: 10.5978/islsm.20-OR-05
Histological investigation of picosecond laser-toning and fractional laser therapy
Abstract
Background and aims: Rejuvenation therapy using picosecond pulse laser and picosecond pulsed fractional therapy with a fractional lens have been performed with clinical effects evaluated. However, no histological analysis of effects on photoaged skin exists. In this study, influence of laser-toning and fractional therapy using picosecond pulse laser on photoaging was histologically investigated.
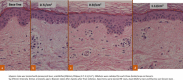
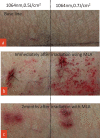
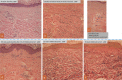
Subjects and methods: The flexor side forearm of a male, age 61, with photoaging was divided into three 20 cm2 areas and irradiated with approximately 400 shots of 10-Hz laser, 8 mm spot size, and nine passes at an output of 0.7, 0.9, and 1.1 J/cm2 using picosecond laser-toning therapy six times, every two weeks. Two weeks post final irradiation, 2 mm punch biopsies were taken from the irradiation fields. Fractional therapy using Micro Lens Array (MLA) attached picosecond fractional therapy was applied to the medial crural skin with marked photoaging of a male, age 63. Irradiation was applied at 0.5 and 0.7 J/cm2 through two passes, with 3 mm punch biopsies taken from each irradiation field immediately after and again two months post-irradiation. Samples were subjected to hematoxylin and eosin (HE) and Elastica van Gieson staining and compared.
Results: In the picosecond laser-toning therapy sample, photoaging-induced dermis reconstruction occurred. The picosecond fractional therapy sample showed both epidermis and dermis reconstruction, with intrinsic aging and photoaging improvements.
Conclusions: Recovery of dermal and epidermal age related atrophy by picosecond laser-toning and picosecond fractional therapy was histologically confirmed. Picosecond fractional therapy demonstrated superior improvement.
Keywords: Picosecond pulsed fractional therapy; Picosecond pulsed laser-toning therapy; Rejuvenation; intrinsic aging; photoaging.
2020, Japan Medical Laser Laboratory.
Figures


References
-
- Lee KC, Wambier CG, Soon SL, Sterling JB, Landau M, Rullan P, Brody HJ. Basic chemical peeling: Superficial and medium-depth peels J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019; 81: 313-324. - PubMed
-
- Lowe Nj, Lask G, Griffin ME, Maxwell A, Lowe P, Quilada F. Skin resurfacing with the ultrapulse carbon dioxide laser. Observation on 100 patients, Dermal Surg. 1995;21:1025-1029. - PubMed
-
- Perez MI, Bank DE, Silvers D. Skin resurfacing of the face with the Erbium:YAG laser. Dermatol Sug. 1998; 24:653-658. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RR, Parrish JA. Selective photothermolysis: Precise microsurgery by selective absorption of pulsed radiation. Science. 1983;220:524. - PubMed
-
- Lee MW. Combination 532-nm and 1064-nm lasers for noninvasive skin rejuvenation and toning. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:1265-1276. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
