Pleomorphic Adenoma: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 32904077
- PMCID: PMC7450192
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1776
Pleomorphic Adenoma: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Pleomorphic adenoma (PA) is a commonly occurring benign tumor originating in the salivary glands.
Objective: The aim was to carry out a systematic literature of reports on pleomorphic adenoma from 2000 to 2018 to determine patient's age spread, gender, anatomical location, capsular invasion, histopathology, treatment and patient outcome.
Materials and methods: A PubMed search was conducted with the following key words: adenoma, pleomorphic adenoma, and mixed salivary tumor.
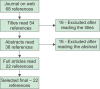
Results: Twenty-two articles in English were read in full after fulfilling the eligibility criteria. The mean age of PA occurrence was 44.14 years with a definite female predilection (M:F ratio = 13:8). It most commonly occurred in the facial region (42.85%), and surgical approach is the preferred intervention.
Conclusion: Pleomorphic adenomas are benign salivary gland neoplasms that can grow into extensive sizes if left untreated and hence need to be diagnosed early. Complete excision of the tumor is the definitive treatment, as enucleation can result in recurrence. Facial nerve has to be preserved if PA occurs in the parotid gland.
How to cite this article: Almeslet AS. Pleomorphic Adenoma: A Systematic Review. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2020;13(3):284-287.
Keywords: Case report; Pleomorphic adenoma; Salivary gland; Tumor.
Copyright © 2020; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retrospective Analysis of Histopathological Reports of Salivary Gland Pleomorphic Adenomas in Tanzania.East Afr Health Res J. 2024;8(2):195-199. doi: 10.24248/eahrj.v8i2.781. Epub 2024 Jun 26. East Afr Health Res J. 2024. PMID: 39296770 Free PMC article.
-
Synchronous Parotid and Homolateral Submandibular Gland Pleomorphic Adenoma.Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 May;31(104):185-190. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 31223600 Free PMC article.
-
[Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of major salivary glands--a clinicopathologic review].Otolaryngol Pol. 2007;61(5):687-93. doi: 10.1016/S0030-6657(07)70507-3. Otolaryngol Pol. 2007. PMID: 18552001 Polish.
-
Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid Gland: Report of a Case With Review of Literature.Ethiop J Health Sci. 2015 Apr;25(2):189-94. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v25i2.13. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2015. PMID: 26124628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metastasising Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid Gland: Where are We Now? A Systematic Literature Review.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2025 Jun;24(3):664-673. doi: 10.1007/s12663-025-02472-w. Epub 2025 Feb 13. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2025. PMID: 40453624 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical behavior of recurrent pleomorphic adenoma in the palate: a systematic review.Acta Cir Bras. 2024 Feb 26;39:e390824. doi: 10.1590/acb390824. eCollection 2024. Acta Cir Bras. 2024. PMID: 38422328 Free PMC article.
-
Bronchial pleomorphic adenoma successfully diagnosed and resected with left lower sleeve lobectomy; a case report and literature review.Respir Med Case Rep. 2025 Jul 2;57:102253. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2025.102253. eCollection 2025. Respir Med Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40688714 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-to-Tumor Metastasis of Lung Cancer to Kidney Cancer: A Review of the Literature and Our Experience.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Mar 5;14(5):553. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14050553. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myoepithelial Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Submandibular Gland: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Mar 3;15(3):e35722. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35722. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37016641 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoexpression of Autophagy-Related Proteins in Salivary Gland Tumors: An Exploratory Study.Head Neck Pathol. 2023 Sep;17(3):589-598. doi: 10.1007/s12105-023-01556-8. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Head Neck Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37118353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rajendran S, Sivapathasundaram S. Shafer's Textbook of Oral Pathology. 6th ed., New Delhi: Elsevier; 2009. pp. 219–224.
-
- Regezi JA, Batsakis JG. Histogenesis of salivary gland neoplasms. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1977;10(2):297–307. - PubMed
-
- Luna MA. Salivary glands. In: Pilch BZ., editor. Head and neck surgical pathology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2001. pp. 284–349.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials