Intraoral Dual Wavelength Laser Diode Therapy for Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis
- PMID: 32904078
- PMCID: PMC7447824
- DOI: 10.5978/islsm.20-OR-06
Intraoral Dual Wavelength Laser Diode Therapy for Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis
Abstract
Background: Chronic sinusitis is one of the most common chronic diseases involving different age groups. The different etiological factors and difficult diagnostic procedures contribute to misdiagnosis and chronicity of sinusitis. There is no standard treatment for sinusitis. Long term use of corticosteroids and antibiotics may lead to numerous adverse side effects. Laser therapy has been suggested as a non-invasive treatment for sinusitis. It has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. When considering maxillary sinusitis, discharge tends to collect in the sinus base due to its anatomy and altered physiology. To improve penetration of laser into the maxillary sinus, intraoral laser at the vestibule depth of the maxilla may be more effective.
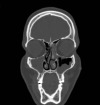
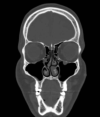
Material and subject: Thirty-four patients with chronic maxillary sinusitis were assigned into two groups. All were assessed before and after treatment. Group A received laser radiation plus standard medical treatment and group B received medical treatment only. The treatment plan was performed in 12 sessions using a Diode laser with a wavelength of 810 nm and 980nm. The SNOT-22 questionnaire and Computed Tomography were used to evaluate patients. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: Both groups showed a significant improvement in symptoms following treatment (p < .001), however, the laser therapy group demonstrated greater improvements for all variables in response to treatment as compared to the traditional treatment group (p < .001).
Conclusions: Using high intensity intra-oral laser therapy with medical treatment is more effective than using medical treatment only for treatment of chronic maxillary sinusitis.
Keywords: High Intensity Laser Therapy (HILT); Maxillary Sinusitis; Sino Nasal Outcome Test (SNOT22).
2020, Japan Medical Laser Laboratory.
Figures
References
-
- Passali D, Cingi C, Cambi J, Passali F, Muluk NB: A survey on chronic rhinosinusitis: Opinions from experts of 50 countries. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016; 273:2097-2109. - PubMed
-
- Anand VK. Epidemiology and economic impact of rhinosinusitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 2004; 193:3-5. - PubMed
-
- Hamilos DL: Chronic rhinosinusitis: epidemiology and medical management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128:693-707. - PubMed
-
- Halawi AM, Smith SS, Chandra RK: Chronic rhinosinusitis: epidemiology and cost. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2013; 34:328-34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources