Robust T Cell Response Toward Spike, Membrane, and Nucleocapsid SARS-CoV-2 Proteins Is Not Associated with Recovery in Critical COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 32904468
- PMCID: PMC7456276
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100092
Robust T Cell Response Toward Spike, Membrane, and Nucleocapsid SARS-CoV-2 Proteins Is Not Associated with Recovery in Critical COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
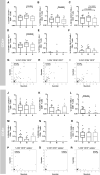
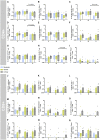
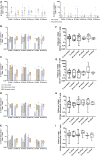
T cell immunity toward SARS-CoV-2 spike (S-), membrane (M-), and nucleocapsid (N-) proteins may define COVID-19 severity. Therefore, we compare the SARS-CoV-2-reactive T cell responses in moderate, severe, and critical COVID-19 patients and unexposed donors. Overlapping peptide pools of all three proteins induce SARS-CoV-2-reactive T cell response with dominance of CD4+ over CD8+ T cells and demonstrate interindividual immunity against the three proteins. M-protein induces the highest frequencies of CD4+ T cells, suggesting its relevance for diagnosis and vaccination. The T cell response of critical COVID-19 patients is robust and comparable or even superior to non-critical patients. Virus clearance and COVID-19 survival are not associated with either SARS-CoV-2 T cell kinetics or magnitude of T cell responses, respectively. Thus, our data do not support the hypothesis of insufficient SARS-CoV-2-reactive immunity in critical COVID-19. Conversely, it indicates that activation of differentiated memory effector T cells could cause hyperreactivity and immunopathogenesis in critical patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; S/M/N protein-reactive T cells; SARS-CoV-2; critical COVID-19; immunity; immunopathology; nucleocapsid; spike.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Crouse J., Kalinke U., Oxenius A. Regulation of antiviral T cell responses by type I interferons. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015;15:231–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

