Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of saline infusion sonohysterography, transvaginal sonography, and hysteroscopy in evaluating the endometrial polyps in women with abnormal uterine bleeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32904526
- PMCID: PMC7457193
- DOI: 10.5114/wiitm.2020.93791
Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of saline infusion sonohysterography, transvaginal sonography, and hysteroscopy in evaluating the endometrial polyps in women with abnormal uterine bleeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: In women with abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB), endometrial polyps are a frequent finding, and the risk of a focal (pre)malignancy in a polyp is up to 6%. Because of this reported risk, the detection of polyps in these women is important.
Aim: To evaluate and compare the diagnostic accuracy of saline infusion sonohysterography, transvaginal sonography, and hysteroscopy in detecting endometrial polyps in women with AUB.
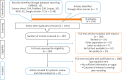
Material and methods: The searches were conducted by two independent researchers to find the relevant studies published from 1/1/2009 until the end of 30/06/2019. We searched for published literature in English language in MEDLINE, EMBASETM, The Cochrane Library, and Trip database. For literature published in other languages, we searched national databases (Magiran and SID), KoreaMed, and LILACS. The risk of bias of every article was evaluated by using QUADAS-2.
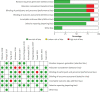
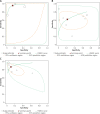
Results: After selection and quality assessment, 11 studies were included. Based on the random effect model the total prevalence of endometrial polyps in women with abnormal uterine bleeding was 38%. The sensitivity and specificity of saline infusion sonohysterography in diagnosis of endometrial polyps were 0.87 and 0.86, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of transvaginal ultrasonography were 0.62 and 0.73 and the sensitivity and specificity of hysteroscopy were 0.92 and 0.85, respectively.
Conclusions: Although that sonohysterography is a safe and relatively cheap method, which allows ruling out or confirming endometrial polyps, it cannot be replaced with hysteroscopy due to the fact that hysteroscopy combined with biopsy is the gold standard for ruling out malignancies in an endometrial polyp.
Keywords: abnormal uterine bleeding; saline infusion sonohysterography; sonohysterography; transvaginal sonography.
Copyright: © 2020 Fundacja Videochirurgii.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Short J, Sharp B, Elliot N, et al. Does the addition of saline infusion sonohysterography to transvaginal ultrasonography prevent unnecessary hysteroscopy in premenopausal women with abnormal uterine bleeding? Aust N Zeal J Obstet Gynaecol. 2016;56:432–5. - PubMed
-
- Inoue T, Kitajima M, Taniguchi K, Masuzaki H. Three-dimensional saline-infusion sonohysterography is useful for the identification of endometrial polyp. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2016;42:855–9. - PubMed
-
- Bradley LD, Gueye NA. The medical management of abnormal uterine bleeding in reproductive-aged women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214:31–44. - PubMed
-
- Shea AK. Comparison of saline infusion sonohysterography and transvaginal ultrasound in detection of endometrial polyps. EC Gynaecol. 2018;7:260–4.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
