Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Sorafenib in Patients with BCLC Stage C Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 32904650
- PMCID: PMC7457560
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S248850
Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Sorafenib in Patients with BCLC Stage C Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) and targeted therapy have become common methods in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of TACE combined with sorafenib (TACE-sorafenib) and TACE alone for the treatment of Barcelona clinical stage C HCC.
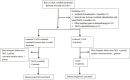
Methods: The clinical data of 75 patients with BCLC stage C HCC who received TACE-sorafenib or TACE as the initial treatment were retrospectively analyzed. Tumor response, time to progression (TTP), overall survival (OS), and adverse events were compared at 1 month after surgery in the two groups.
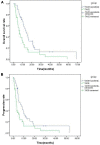
Results: One month after treatment, the disease control rate in the TACE-sorafenib group was higher than that in the TACE group alone (82.76% and 57.50%, respectively, P = 0.018). The median values of TTP and OS in the TACE-sorafenib group were longer than those in the TACE group (TTP was 7.6 and 3.4 months, respectively, P = 0.002; OS was 13.6 and 6.3 months, respectively, P = 0.041). The cumulative survival time at 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year was higher in the TACE-sorafenib group than in the TACE group (83.5%, 71.2%, 45.7% vs 57.4%, 40.6%, 21.2%). Sorafenib-related side effects such as hypertension, hand-foot syndrome, and oral ulcers were more common than those in the TACE group alone (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Compared with TACE treatment alone, TACE combined with sorafenib in BCLC-C stage HCC significantly improved disease control rate, TTP, and OS, and no significant increase in adverse reactions was observed.
Keywords: TACE; hepatocellular carcinoma; sorafenib; survival.
© 2020 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the efficacy and safety of Transarterial chemoembolization with and without Apatinib for the treatment of BCLC stage C hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 19;18(1):1131. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5081-3. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30453925 Free PMC article.
-
Overall survival in response to sorafenib with transarterial chemoembolization for BCLC stage B hepatocellular carcinoma: propensity score analysis .Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Jun;55(6):498-508. doi: 10.5414/CP202787. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28157070
-
Prognosis of transarterial chemoembolization-sorafenib compared to transarterial chemoembolization-alone in hepatocellular carcinoma stage C: a systematic review.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2024 May 27;36(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s43046-024-00224-4. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2024. PMID: 38797810
-
Sorafenib combined with transarterial chemoembolization versus transarterial chemoembolization alone for advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matching study.PLoS One. 2014 May 9;9(5):e96620. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096620. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24817002 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of sorafenib plus transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in treating hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: A meta-analysis.Acta Pharm. 2024 Sep 14;74(3):405-422. doi: 10.2478/acph-2024-0019. Print 2024 Sep 1. Acta Pharm. 2024. PMID: 39279524
Cited by
-
A multi-institutional study to predict the benefits of DEB-TACE and molecular targeted agent sequential therapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma using a radiological-clinical nomogram.Radiol Med. 2024 Jan;129(1):14-28. doi: 10.1007/s11547-023-01736-0. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Radiol Med. 2024. PMID: 37863847
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of molecular targeted agents combined with transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a network meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 May 17;13:1179431. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1179431. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37265792 Free PMC article.
-
External radiotherapy combined with sorafenib has better efficacy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Sep;23(5):1537-1549. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00972-4. Epub 2022 Dec 10. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36495367 Free PMC article.
-
A case of multiple hepatocellular carcinoma experiencing complete responses to sorafenib and atezolizumab-bevacizumab and developing severe, refractory venous congestive cutaneous ulcers on either regimen.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr;16(2):229-236. doi: 10.1007/s12328-023-01756-3. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36624210
-
Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Combined With Sorafenib versus TACE in Patients With BCLC Stage C Hepatocellular Carcinoma - A Retrospective Study.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022 May-Jun;12(3):745-754. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2021.12.009. Epub 2021 Dec 21. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35677519 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous