Coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19) and its natural environmental impacts
- PMID: 32904898
- PMCID: PMC7459942
- DOI: 10.1007/s13762-020-02910-x
Coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19) and its natural environmental impacts
Abstract
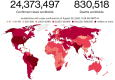
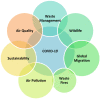
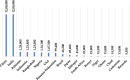
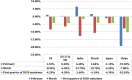
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) is the official name of a respiratory infectious disease caused by a new coronavirus that started first in Wuhan, China, and outspread worldwide with an unexpectedly fast speed. Flights have been canceled worldwide and transportation has been closed nationwide and across international borders. As a consequence, the economic activity has been stopped and stock markets have been dropped. The COVID-19 lockdown has several social and economic effects. Additionally, COVID-19 has caused several impacts on global migration. On the other hand, such lockdown, along with minimal human mobility, has impacted the natural environment somewhat positively. Overall carbon emissions have dropped, and the COVID-19 lockdown has led to an improvement in air quality and a reduction in water pollution in many cities around the globe. A summary of the existing reports of the environmental impacts of COVID-19 pandemic are discussed and the important findings are presented focusing on several aspects: air pollution, waste management, air quality improvements, waste fires, wildlife, global migration, and sustainability.
Keywords: Air pollution; CO2 emissions; Coronavirus pandemic; Economics; Environmental impacts.
© Islamic Azad University (IAU) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
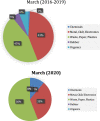
References
-
- Abbasi F, Samaei MR, Manoochehri Z, Jalili M, Yazdani E. The effect of incubation temperature and growth media on index microbial fungi of indoor air in a hospital building in Shiraz, Iran. J Build Eng. 2020;31:101294. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101294. - DOI
-
- Annual State of the Global Air Report (2019) How clean is your air? https://www.stateofglobalair.org/air
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
