Transthoracic echocardiography during prone position ventilation: Lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 32904955
- PMCID: PMC7461552
- DOI: 10.1002/emp2.12239
Transthoracic echocardiography during prone position ventilation: Lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
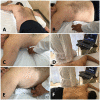
Objective: The current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19 outbreak) demands an increased need for hospitalizations in emergency departments (EDs) and critical care units. Owing to refractory hypoxemia, prone position ventilation has been used more frequently and patients will need repeated hemodynamic assessments. Our main objective was to show the feasibility of obtaining images to measure multiple parameters with transthoracic echocardiography during the prone position ventilation.
Methods: We enrolled 15 consecutive mechanically ventilated patients with confirmed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection that required prone position ventilation as a rescue maneuver for refractory hypoxemia. The studies were performed by 2 operators with training in critical care echocardiography. Measurements were done outside the patient's room and the analysis of the images was performed by 3 cardiologists with training in echocardiography.
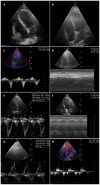
Results: Adequate image acquisition of the left ventricle was possible in all cases; we were not able to visualize the right ventricular free wall only in 1 patient. The mean tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion was 17.8 mm, tricuspid peak systolic S wave tissue Doppler velocity 11.5 cm/s, and the right ventricular basal diameter 36.6 mm; left ventricle qualitative function was reduced in 6 patients; pericardial effusion or valvular abnormalities were not observed.
Conclusion: We showed that echocardiographic images can be obtained to measure multiple parameters during the prone position ventilation. This technique has special value in situations where there is sudden hemodynamic deterioration and it is not possible to return the patient in the supine position.
Keywords: echocardiography; mechanical ventilation; prone position.
© 2020 The Authors. JACEP Open published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Mitchell C, Rahko PS, Blauwet LA, et al. Guidelines for performing a comprehensive transthoracic echocardiographic examination in adults: recommendations from the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2019;32:1‐64. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

