Combined Point-of-Care Nucleic Acid and Antibody Testing for SARS-CoV-2 following Emergence of D614G Spike Variant
- PMID: 32905045
- PMCID: PMC7462534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100099
Combined Point-of-Care Nucleic Acid and Antibody Testing for SARS-CoV-2 following Emergence of D614G Spike Variant
Abstract
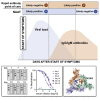
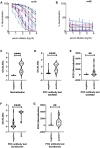
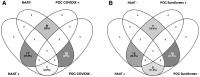
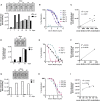
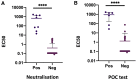
Rapid COVID-19 diagnosis in the hospital is essential, although this is complicated by 30%-50% of nose/throat swabs being negative by SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT). Furthermore, the D614G spike mutant dominates the pandemic and it is unclear how serological tests designed to detect anti-spike antibodies perform against this variant. We assess the diagnostic accuracy of combined rapid antibody point of care (POC) and nucleic acid assays for suspected COVID-19 disease due to either wild-type or the D614G spike mutant SARS-CoV-2. The overall detection rate for COVID-19 is 79.2% (95% CI 57.8-92.9) by rapid NAAT alone. The combined point of care antibody test and rapid NAAT is not affected by D614G and results in very high sensitivity for COVID-19 diagnosis with very high specificity.
Keywords: COVID-19; D614G; SARS-CoV-2; point of care testing; rapid diagnoses.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Collier D.A., Assennato S.M., Warne B., Sithole N., Sharrocks K., Ritchie A., Ravji P., Routledge M., Sparkes D., Skittrall J. Point of Care Nucleic Acid Testing for SARS-CoV-2 in Hospitalized Patients: A Clinical Validation Trial and Implementation Study. Cell Rep. Med. 2020;1:100062. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arevalo-Rodriguez I., Buitrago-Garcia D., Simancas-Racines D., Zambrano-Achig P., del Campo R., Ciapponi A., Sued O., Martinez-Garcia L., Rutjes L., Low N. False-negative results of initial RT-PCR assays for COVID-19: a systematic review. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.04.16.20066787. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

