Effects of galloflavin and ellagic acid on sirtuin 6 and its anti-tumorigenic activities
- PMID: 32905943
- PMCID: PMC12036747
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110701
Effects of galloflavin and ellagic acid on sirtuin 6 and its anti-tumorigenic activities
Abstract
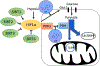
Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6), a member of sirtuin family (SIRT1-7), regulates distinct cellular functions; genome stability, DNA repair, and inflammation related diseases. Recently, we demonstrated that anthocyanidins in berries induce the catalytic activity of SIRT6. In this study, we explored the effects of Galloflavin and Ellagic acid, the most common polyphenols in berries, on SIRT6. SIRT6 deacetylation was investigated using HPLC and immunoblotting assays. The expression levels of SIRT6, glycolytic proteins and cellular metabolism were studied on human colon adenocarcinoma cells (Caco2). Molecular docking studies were carried out to study possible interactions of the compounds with sirtuins. Ellagic acid increased the deacetylase activity of SIRT6 by up to 50-fold; it showed moderate inhibition of SIRT1-3. Galloflavin and Ellagic acid showed anti-proliferative effects on Caco2. The compounds also upregulated SIRT6 expression whereas key proteins in glycolysis were downregulated. Galloflavin decreased glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) expression, and Ellagic acid affected the expression of protein dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1). Interestingly, both compounds caused reduction in glucose uptake and lactate production. Both Galloflavin and Ellagic acid were able to form hydrogen bonds with Asp188 and Gly6 in SIRT6. In this study, we showed that Galloflavin and Ellagic acid increased SIRT6 activity and decreased the expression of SIRT6 associated proteins involved in cancer development. Taken together, Galloflavin and Ellagic acid targeting SIRT6 activity may provide a new insight in the development of anti-cancer therapy.
Keywords: Berries; Cancer; Polyphenol; Sirtuin; Tannin.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Figures






Similar articles
-
Screening of SIRT6 inhibitors and activators: A novel activator has an impact on breast cancer cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jun;138:111452. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111452. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33684691 Free PMC article.
-
Natural polyphenols as sirtuin 6 modulators.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 7;8(1):4163. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22388-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29515203 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT6 deacetylase transcriptionally regulates glucose metabolism in heart.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jul;233(7):5478-5489. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26434. Epub 2018 Feb 22. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29319170
-
Biological and catalytic functions of sirtuin 6 as targets for small-molecule modulators.J Biol Chem. 2020 Aug 7;295(32):11021-11041. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.011438. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32518153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuin 6: a review of biological effects and potential therapeutic properties.Mol Biosyst. 2013 Jul;9(7):1789-806. doi: 10.1039/c3mb00001j. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Mol Biosyst. 2013. PMID: 23592245 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment Strategies and Metabolic Pathway Regulation in Urothelial Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 26;21(23):8993. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238993. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33256165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening of SIRT6 inhibitors and activators: A novel activator has an impact on breast cancer cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jun;138:111452. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111452. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33684691 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate-mediated metabolic reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages: implications for tumor progression and therapeutic potential.Front Immunol. 2025 May 13;16:1573039. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1573039. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40433363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular Pathways and Mechanisms of Colored Secondary Metabolites in Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 1;23(17):9943. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179943. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ellagic Acid and Cancer Hallmarks: Insights from Experimental Evidence.Biomolecules. 2023 Nov 15;13(11):1653. doi: 10.3390/biom13111653. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38002335 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

