Synthesis of Carbon Nanomaterials from Biomass Utilizing Ionic Liquids for Potential Application in Solar Energy Conversion and Storage
- PMID: 32906574
- PMCID: PMC7558495
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13183945
Synthesis of Carbon Nanomaterials from Biomass Utilizing Ionic Liquids for Potential Application in Solar Energy Conversion and Storage
Abstract
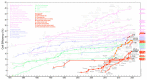
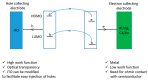
Considering its availability, renewable character and abundance in nature, this review assesses the opportunity of the application of biomass as a precursor for the production of carbon-based nanostructured materials (CNMs). CNMs are exceptionally shaped nanomaterials that possess distinctive properties, with far-reaching applicability in a number of areas, including the fabrication of sustainable and efficient energy harnessing, conversion and storage devices. This review describes CNM synthesis, properties and modification, focusing on reports using biomass as starting material. Since biomass comprises 60-90% cellulose, the current review takes into account the properties of cellulose. Noting that highly crystalline cellulose poses a difficulty in dissolution, ionic liquids (ILs) are proposed as the solvent system to dissolve the cellulose-containing biomass in generating precursors for the synthesis of CNMs. Preliminary results with cellulose and sugarcane bagasse indicate that ILs can not only be used to make the biomass available in a liquefied form as required for the floating catalyst CVD technique but also to control the heteroatom content and composition in situ for the heteroatom doping of the materials.
Keywords: biomass; carbon-based nanostructured material; cellulose; energy; ionic liquids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

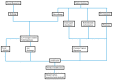
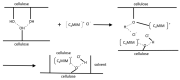
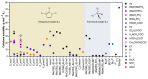
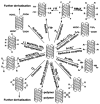
References
-
- Kroto H.W., Heath J.R., O′Brien S.C., Curl R.F., Smalley R.E. C 60: Buckminsterfullerene. Nature. 1985;318:162–163. doi: 10.1038/318162a0. - DOI
-
- Iijima S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature. 1991;354:56–58. doi: 10.1038/354056a0. - DOI
-
- Gspann T.S., Juckes S.M., Niven J.F., Johnson M.B., Elliott J.A., White M.A., Windle A.H. High thermal conductivities of carbon nanotube films and micro-fibres and their dependence on morphology. Carbon. 2017;114:160–168. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.12.006. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

