Valorization of Sweet Lime Peel for the Extraction of Essential Oil by Solvent Free Microwave Extraction Enhanced with Ultrasound Pretreatment
- PMID: 32906576
- PMCID: PMC7570843
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25184072
Valorization of Sweet Lime Peel for the Extraction of Essential Oil by Solvent Free Microwave Extraction Enhanced with Ultrasound Pretreatment
Abstract
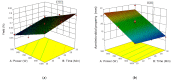
Essential oils of sweet lime peel, a waste by-product in the juice industry, were extracted using the vacuum assisted solvent free microwave extraction (VASFME) method. The effects of microwave output power (500-1000 W) and extraction time (20-30 min) on the essential oils yield and antimicrobial property were investigated. Optimal conditions were observed at 797.844 W microwave output power and 30 min extraction time. The essential oils yield and antimicrobial property under these conditions were 0.792 ± 0.03% and 18.25 ± 1.45 mm, respectively, which agrees with the predicted values of 0.757% and 16.50 mm. The essential oils were extracted at optimized conditions and analyzed through GCMS for compound identification. A total of 49 compounds were identified, with limonene content (43.47%) being the highest among all sweet lime peel oil compounds. Moreover, the sweet lime peels were subjected to ultrasound pre-treatment before microwave extraction. The ultrasound pre-treatment helped to increase the essential oils yield from 0.84 to 1.06% as the treatment time increased from 30 to 90 min. The increase in yield was 37.66% more compared to VASFME at 90 min treatment time.
Keywords: antimicrobial activity; essential oil; microwave extraction; sweet lime peel; ultrasound treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Megha M., Mumtaj S. Extraction and characterization of essential oil of sweet lime (Citrus limetta risso) peel using microwave-assisted hydrodistillation. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2014;4:51–55.
-
- Farhat A., Fabiano-Tixier A.-S., Maataoui M., Maingonnat J.-F., Romdhane M., Chemat F. Microwave steam diffusion for extraction of essential oil from orange peel: Kinetic data, extract’s global yield and mechanism. Food Chem. 2011;125:255–261. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.07.110. - DOI
-
- Colecio-Juárez M.C., Rubio-Núñez R.E., Botello-Álvarez J.E., Martínez-González G.M., Navarrete-Bolaños J.L., Jiménez-Islas H. Characterization of volatile compounds in the essential oil of sweet lime (Citrus limetta Risso) Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2012;72:275–280. doi: 10.4067/S0718-58392012000200017. - DOI
-
- Mahmud S., Saleem M., Siddique S., Ahmed R., Khanum R., Perveen Z. Volatile components, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of Citrus acida var. sour lime peel oil. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2009;13:195–198. doi: 10.1016/j.jscs.2009.03.001. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials