Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa subsp. sativa) as an Emerging Source for Value-Added Functional Food Ingredients and Nutraceuticals
- PMID: 32906622
- PMCID: PMC7571072
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25184078
Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa subsp. sativa) as an Emerging Source for Value-Added Functional Food Ingredients and Nutraceuticals
Abstract
Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Cannabaceae) is an ancient cultivated plant originating from Central Asia and historically has been a multi-use crop valued for its fiber, food, and medicinal uses. Various oriental and Asian cultures kept records of its production and numerous uses. Due to the similarities between industrial hemp (fiber and grain) and the narcotic/medical type of Cannabis, the production of industrial hemp was prohibited in most countries, wiping out centuries of learning and genetic resources. In the past two decades, most countries have legalized industrial hemp production, prompting a significant amount of research on the health benefits of hemp and hemp products. Current research is yet to verify the various health claims of the numerous commercially available hemp products. Hence, this review aims to compile recent advances in the science of industrial hemp, with respect to its use as value-added functional food ingredients/nutraceuticals and health benefits, while also highlighting gaps in our current knowledge and avenues of future research on this high-value multi-use plant for the global food chain.
Keywords: CBD; Cannabis sativa; cannabinoids; health benefits; hemp seed oil; oil extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
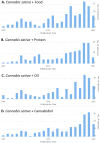
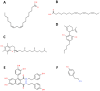

References
-
- Vonapartis E., Aubin M.P., Seguin P., Mustafa A.F., Charron J.B. Seed composition of ten industrial hemp cultivars approved for production in Canada. J. Food Composit. Anal. 2015;39:8–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2014.11.004. - DOI
-
- Callaway J.C. Hempseed as a nutritional resource: An overview. Euphytica. 2004;140:65–72. doi: 10.1007/s10681-004-4811-6. - DOI
-
- Struik P.C., Amaducci S., Bullard M.J., Stutterheim N.C., Venturi G., Cromack H.T.H. Agronomy of fibre hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) in Europe. Ind. Crops Prod. 2000;11:107–118. doi: 10.1016/S0926-6690(99)00048-5. - DOI
-
- Ranalli P., Venturi G. Hemp as a raw material for industrial applications. Euphytica. 2004;140:1–6. doi: 10.1007/s10681-004-4749-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

