Impedimetric Sensing of Factor V Leiden Mutation by Zip Nucleic Acid Probe and Electrochemical Array
- PMID: 32906640
- PMCID: PMC7559847
- DOI: 10.3390/bios10090116
Impedimetric Sensing of Factor V Leiden Mutation by Zip Nucleic Acid Probe and Electrochemical Array
Abstract
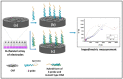
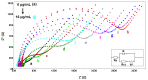
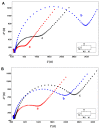
A carbon nanofiber enriched 8-channel screen-printed electrochemical array was used for the impedimetric detection of SNP related to Factor V Leiden (FV Leiden) mutation, which is the most common inherited form of thrombophilia. FV Leiden mutation sensing was carried out in three steps: solution-phase nucleic acid hybridization between zip nucleic acid probe (Z-probe) and mutant type DNA target, followed by the immobilization of the hybrid on the working electrode area of array, and measurement by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). TArzhe selectivity of the assay was tested against mutation-free DNA sequences and synthetic polymerase chain reaction (PCR) samples. The developed biosensor was a trustful assay for FV Leiden mutation diagnosis, which can effectively discriminate wild type and mutant type even in PCR samples.
Keywords: 8-channel screen-printed electrochemical arrays; SNP; electrochemical impedance spectroscopy; zip nucleic acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

