pH-Responsive and Biodegradable ZnO-Capped Mesoporous Silica Composite Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery
- PMID: 32906723
- PMCID: PMC7558045
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13183950
pH-Responsive and Biodegradable ZnO-Capped Mesoporous Silica Composite Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery
Abstract
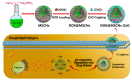
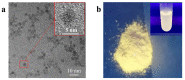
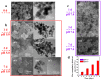
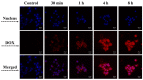
As a drug delivery system (DDS), traditional mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) suffer from bioaccumulation in vivo and premature drug release in systemic circulation due to low degradation rate and lack of protective gatekeeper. Herein, we developed a safe and intelligent DDS with characteristics of pH-responsive biodegradation and controlled drug release based on mesoporous silica composite nanoparticles (MSCNs) capped with ZnO quantum dots (ZnO QDs). Acidic degradable MSCNs were successfully synthesized by doping Ca2+ and PO43- into the MSNs' framework. The in vitro doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) release was inhibited at neutral pH 7.4 but triggered significantly at pH 5.0 due to the dissociation of ZnO caps. The internalization behavior and cytotoxicity of 4T1 cells indicated MSCNs-ZnO could efficiently deliver DOX into the cells with significant antitumor activity. Such a DDS with pH-responsive biodegradation and controlled drug release has promising potential for cancer therapy.
Keywords: ZnO QDs; mesoporous silica composite nanoparticles (MSCNs); pH-responsive biodegradability; pH-responsive drug delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Based on Charge-Reversal Plug-Gate Nanovalves and Acid-Decomposable ZnO Quantum Dots for Intracellular Drug Delivery.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Dec 9;7(48):26666-73. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b08460. Epub 2015 Nov 23. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 26553405
-
Poly(amino acid)/ZnO/mesoporous silica nanoparticle based complex drug delivery system with a charge-reversal property for cancer therapy.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019 Sep 1;181:461-469. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.05.078. Epub 2019 May 31. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019. PMID: 31176118
-
pH-Sensitive ZnO Quantum Dots-Doxorubicin Nanoparticles for Lung Cancer Targeted Drug Delivery.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016 Aug 31;8(34):22442-50. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b04933. Epub 2016 Aug 19. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016. PMID: 27463610
-
pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles employed in controlled drug delivery systems for cancer treatment.Cancer Biol Med. 2014 Mar;11(1):34-43. doi: 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2014.01.003. Cancer Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 24738037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Biopolymers as Smart Coating Materials of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 29;15(2):447. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020447. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839771 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies to Regulate the Degradation and Clearance of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jun 13;19:5859-5878. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S451919. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38887691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Efficient Nanocarriers for Targeted Cancer Therapy: Addressing Chemotherapy-Induced Disabilities.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 19;16(24):4234. doi: 10.3390/cancers16244234. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery: where are we after two decades?Chem Soc Rev. 2022 Jul 4;51(13):5365-5451. doi: 10.1039/d1cs00659b. Chem Soc Rev. 2022. PMID: 35642539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Agents for Cancer Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jan 24;13(2):152. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020152. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33498885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
pH-Responsive Pesticide-Loaded Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with ZnO Quantum Dots as a Gatekeeper for Control of Rice Blast Disease.Materials (Basel). 2024 Mar 14;17(6):1344. doi: 10.3390/ma17061344. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38541498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen X., Yao X., Wang C., Chen L., Chen X. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles capped with fluorescence-conjugated cyclodextrin for pH-activated controlled drug delivery and imaging. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015;217:46–53. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.06.012. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

