Automated classification of protein subcellular localization in immunohistochemistry images to reveal biomarkers in colon cancer
- PMID: 32907537
- PMCID: PMC7487883
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-020-03731-y
Automated classification of protein subcellular localization in immunohistochemistry images to reveal biomarkers in colon cancer
Abstract
Background: Protein biomarkers play important roles in cancer diagnosis. Many efforts have been made on measuring abnormal expression intensity in biological samples to identity cancer types and stages. However, the change of subcellular location of proteins, which is also critical for understanding and detecting diseases, has been rarely studied.
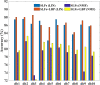
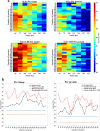
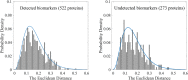
Results: In this work, we developed a machine learning model to classify protein subcellular locations based on immunohistochemistry images of human colon tissues, and validated the ability of the model to detect subcellular location changes of biomarker proteins related to colon cancer. The model uses representative image patches as inputs, and integrates feature engineering and deep learning methods. It achieves 92.69% accuracy in classification of new proteins. Two validation datasets of colon cancer biomarkers derived from published literatures and the human protein atlas database respectively are employed. It turns out that 81.82 and 65.66% of the biomarker proteins can be identified to change locations.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that using image patches and combining predefined and deep features can improve the performance of protein subcellular localization, and our model can effectively detect biomarkers based on protein subcellular translocations. This study is anticipated to be useful in annotating unknown subcellular localization for proteins and discovering new potential location biomarkers.
Keywords: Bioimage processing; Bioinformatics; Cancer biomarkers; Machine learning; Protein subcellular location.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Automated classification of protein expression levels in immunohistochemistry images to improve the detection of cancer biomarkers.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Nov 8;23(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-05015-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36348299 Free PMC article.
-
Automated analysis of immunohistochemistry images identifies candidate location biomarkers for cancers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Dec 23;111(51):18249-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415120112. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25489103 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporating label correlations into deep neural networks to classify protein subcellular location patterns in immunohistochemistry images.Proteins. 2022 Feb;90(2):493-503. doi: 10.1002/prot.26244. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Proteins. 2022. PMID: 34546597
-
A review of image analysis and machine learning techniques for automated cervical cancer screening from pap-smear images.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018 Oct;164:15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.05.034. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018. PMID: 30195423 Review.
-
A review from biological mapping to computation-based subcellular localization.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Apr 20;32:507-521. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.04.015. eCollection 2023 Jun 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023. PMID: 37215152 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual-Signal Feature Spaces Map Protein Subcellular Locations Based on Immunohistochemistry Image and Protein Sequence.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 7;23(22):9014. doi: 10.3390/s23229014. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005402 Free PMC article.
-
Automated classification of protein expression levels in immunohistochemistry images to improve the detection of cancer biomarkers.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Nov 8;23(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-05015-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36348299 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Prediction of Subcellular Localization of Proteins and Related Topics.Front Bioinform. 2022 May 19;2:910531. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2022.910531. eCollection 2022. Front Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 36304291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Learning Approaches for Automatic Localization in Medical Images.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 29;2022:6347307. doi: 10.1155/2022/6347307. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35814554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review for Artificial Intelligence Based Protein Subcellular Localization.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 27;14(4):409. doi: 10.3390/biom14040409. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672426 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Breker M, Schuldiner M. The emergence of proteome-wide technologies: systematic analysis of proteins comes of age. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(7):453–464. - PubMed
-
- Hung MC, Link W. Protein localization in disease and therapy. J Cell Sci. 2011;124(20):3381–3392. - PubMed
-
- Casanova I, Parreno M, Farre L, Guerrero S, Cespedes MV, Pavon MA, et al. Celecoxib induces anoikis in human colon carcinoma cells associated with the deregulation of focal adhesions and nuclear translocation of p130Cas. Int J Cancer. 2006;118(10):2381–2389. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

