A three-arm, multicenter, open-label randomized controlled trial of hydroxychloroquine and low-dose prednisone to treat recurrent pregnancy loss in women with undifferentiated connective tissue diseases: protocol for the Immunosuppressant regimens for LIving FEtuses (ILIFE) trial
- PMID: 32907619
- PMCID: PMC7488113
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-020-04716-1
A three-arm, multicenter, open-label randomized controlled trial of hydroxychloroquine and low-dose prednisone to treat recurrent pregnancy loss in women with undifferentiated connective tissue diseases: protocol for the Immunosuppressant regimens for LIving FEtuses (ILIFE) trial
Abstract
Background: Undifferentiated connective tissue disease (UCTD) is known to induce adverse pregnancy outcomes and even recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA) by placental vascular damage and inflammation activation. Anticoagulation can prevent pregnancy morbidities. However, it is unknown whether the addition of immune suppressants to anticoagulation can prevent spontaneous pregnancy loss in UCTD patients. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and low-dose prednisone on recurrent pregnancy loss for women with UCTD.
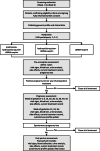
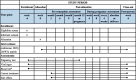
Methods: The Immunosuppressant for Living Fetuses (ILIFE) Trial is a three-arm, multicenter, open-label randomized controlled trial with the primary objective of comparing hydroxychloroquine combined with low-dose prednisone and anticoagulation with anticoagulation alone in treating UCTD women with recurrent spontaneous abortion. The third arm of using hydroxychloroquine combined with anticoagulant for secondary comparison. A total of 426 eligible patients will be randomly assigned to each of the three arms with a 1:1:1 allocation ratio. The primary outcome is the rate of live births. Secondary outcomes include adverse pregnancy outcomes and progression of UCTD.
Discussion: This is the first multi-center, open-label, randomized controlled trial which evaluates the efficacy of immunosuppressant regimens on pregnancy outcomes and UCTD progression. It will provide evidence on whether the immunosuppressant ameliorates the pregnancy prognosis in UCTD patients with RSA and the progression into defined connective tissue disease.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03671174 . Registered on 14 September 2018.
Keywords: Hydroxychloroquine; Prednisone; Randomized controlled trial; Recurrent pregnancy loss; Recurrent spontaneous abortion; Undifferentiated connective tissue disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Mosca M, Neri R, Bombardieri S. Undifferentiated connective tissue diseases (UCTD): a review of the literature and a proposal for preliminary classification criteria. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1999;17(5):615–620. - PubMed
-
- Vaz CC, Couto M, Medeiros D, Miranda L, Costa J, Nero P, et al. Undifferentiated connective tissue disease: a seven-center cross-sectional study of 184 patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2009;28(8):915–921. - PubMed
-
- Guerrero LF, Rueda JC, Arciniegas R, Rueda JM. Undifferentiated connective tissue disease in a rheumatology center in Cali, Colombia: clinical features of 94 patients followed for a year. Rheumatol Int. 2013;33(4):1085–1088. - PubMed
-
- Spinillo A, Beneventi F, Ramoni V, Caporali R, Locatelli E, Simonetta M, et al. Prevalence and significance of previously undiagnosed rheumatic diseases in pregnancy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(6):918–923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical