MicroRNAs and obesity-induced endothelial dysfunction: key paradigms in molecular therapy
- PMID: 32907629
- PMCID: PMC7488343
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-020-01107-3
MicroRNAs and obesity-induced endothelial dysfunction: key paradigms in molecular therapy
Abstract
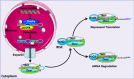
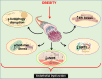
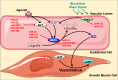
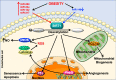
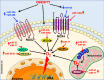
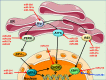
The endothelium plays a pivotal role in maintaining vascular health. Obesity is a global epidemic that has seen dramatic increases in both adult and pediatric populations. Obesity perturbs the integrity of normal endothelium, leading to endothelial dysfunction which predisposes the patient to cardiovascular diseases. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules that play important roles in a variety of cellular processes such as differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, and stress response; their alteration contributes to the development of many pathologies including obesity. Mediators of obesity-induced endothelial dysfunction include altered endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), oxidative stress, autophagy machinery and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. All of these factors have been shown to be either directly or indirectly caused by gene regulatory mechanisms of miRNAs. In this review, we aim to provide a comprehensive description of the therapeutic potential of miRNAs to treat obesity-induced endothelial dysfunction. This may lead to the identification of new targets for interventions that may prevent or delay the development of obesity-related cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; Endothelial dysfunction; MicroRNAs; Obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of the Diabetic Environment On the Expression of MiRNAs in Endothelial Cells: Mir-149-5p Restoration Ameliorates the High Glucose-Induced Expression of TNF-α and ER Stress Markers.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(1):120-135. doi: 10.1159/000480330. Epub 2017 Aug 28. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28848152
-
Oxidative Stress-Induced miR-200c Disrupts the Regulatory Loop Among SIRT1, FOXO1, and eNOS.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017 Aug 20;27(6):328-344. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6643. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017. PMID: 27960536
-
Mechanisms linking endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and microRNAs to adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Oct;56(5):455-481. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2021.1925219. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34182855 Review.
-
Sirtuin 1 is upregulated in young obese Zucker rat cerebral arteries.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 5;721(1-3):43-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.09.057. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24113524
-
Posttranscriptional and transcriptional regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase during hypoxia: the role of microRNAs.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2016 Sep 6;21:16. doi: 10.1186/s11658-016-0017-x. eCollection 2016. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2016. PMID: 28536619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetics in obesity: Mechanisms and advances in therapies based on natural products.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2024 Feb;12(1):e1171. doi: 10.1002/prp2.1171. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2024. PMID: 38293783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mTORC1 (Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1) Signaling in Endothelial and Smooth Muscle Cells Is Required for Vascular Function.Hypertension. 2021 Feb;77(2):594-604. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.14708. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Hypertension. 2021. PMID: 33356400 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in epigenetics of obesity.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022 Nov 17;14(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00947-1. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022. PMID: 36397166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulation of cardiac intermediary metabolism by NADPH oxidases.Cardiovasc Res. 2023 Jan 18;118(17):3305-3319. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvac030. Cardiovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 35325070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond the index: unpacking CVAI's role in cardio-renal-metabolic risk.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Aug 17. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04739-0. Online ahead of print. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40819329 No abstract available.
References
-
- Khan LK, Bowman B. Obesity: a major global public health problem. Ann Rev Nutr. 1999;19:11. - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KMJJ. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999-2004. JAMA. 2006;295:1549–1555. - PubMed
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LRJJ. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. Jama-J Am Med Assoc. 2010;303:235–241. - PubMed
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CLJJ. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. Jama-J Am Med Assoc. 2002;288:1723–1727. - PubMed
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kuczmarski RJ, Johnson CLJ. Overweight and obesity in the United States: prevalence and trends, 1960–1994. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998;22:39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

