De novo design of picomolar SARS-CoV-2 miniprotein inhibitors
- PMID: 32907861
- PMCID: PMC7857403
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abd9909
De novo design of picomolar SARS-CoV-2 miniprotein inhibitors
Abstract
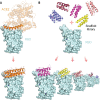
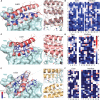
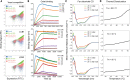
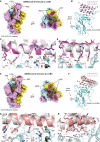
Targeting the interaction between the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein and the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor is a promising therapeutic strategy. We designed inhibitors using two de novo design approaches. Computer-generated scaffolds were either built around an ACE2 helix that interacts with the spike receptor binding domain (RBD) or docked against the RBD to identify new binding modes, and their amino acid sequences were designed to optimize target binding, folding, and stability. Ten designs bound the RBD, with affinities ranging from 100 picomolar to 10 nanomolar, and blocked SARS-CoV-2 infection of Vero E6 cells with median inhibitory concentration (IC50) values between 24 picomolar and 35 nanomolar. The most potent, with new binding modes, are 56- and 64-residue proteins (IC50 ~ 0.16 nanograms per milliliter). Cryo-electron microscopy structures of these minibinders in complex with the SARS-CoV-2 spike ectodomain trimer with all three RBDs bound are nearly identical to the computational models. These hyperstable minibinders provide starting points for SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
Update of
-
De novo design of picomolar SARS-CoV-2 miniprotein inhibitors.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Aug 3:2020.08.03.234914. doi: 10.1101/2020.08.03.234914. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Science. 2020 Oct 23;370(6515):426-431. doi: 10.1126/science.abd9909. PMID: 32793905 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Hou Y. J., Okuda K., Edwards C. E., Martinez D. R., Asakura T., Dinnon K. H. 3rd, Kato T., Lee R. E., Yount B. L., Mascenik T. M., Chen G., Olivier K. N., Ghio A., Tse L. V., Leist S. R., Gralinski L. E., Schäfer A., Dang H., Gilmore R., Nakano S., Sun L., Fulcher M. L., Livraghi-Butrico A., Nicely N. I., Cameron M., Cameron C., Kelvin D. J., de Silva A., Margolis D. M., Markmann A., Bartelt L., Zumwalt R., Martinez F. J., Salvatore S. P., Borczuk A., Tata P. R., Sontake V., Kimple A., Jaspers I., O’Neal W. K., Randell S. H., Boucher R. C., Baric R. S., SARS-CoV-2 reverse genetics reveals a variable infection gradient in the respiratory tract. Cell 182, 429–446.e14 (2020). 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.042 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shi R., Shan C., Duan X., Chen Z., Liu P., Song J., Song T., Bi X., Han C., Wu L., Gao G., Hu X., Zhang Y., Tong Z., Huang W., Liu W. J., Wu G., Zhang B., Wang L., Qi J., Feng H., Wang F. S., Wang Q., Gao G. F., Yuan Z., Yan J., A human neutralizing antibody targets the receptor-binding site of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 584, 120–124 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2381-y - DOI - PubMed
-
- D. Pinto, Y.-J. Park, M. Beltramello, A. C. Walls, M. A. Tortorici, S. Bianchi, S. Jaconi, K. Culap, F. Zatta, A. De Marco, A. Peter, B. Guarino, R. Spreafico, E. Cameroni, J. B. Case, R. E. Chen, C. Havenar-Daughton, G. Snell, A. Telenti, H. W. Virgin, A. Lanzavecchia, M. S. Diamond, K. Fink, D. Veesler, D. Corti, Structural and functional analysis of a potent sarbecovirus neutralizing antibody. bioRxiv 023903 [Preprint] 10 April 2020; 10.1101/2020.04.07.023903. 10.1101/2020.04.07.023903 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

