Dynamic structural order of a low-complexity domain facilitates assembly of intermediate filaments
- PMID: 32907935
- PMCID: PMC7519307
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2010000117
Dynamic structural order of a low-complexity domain facilitates assembly of intermediate filaments
Abstract
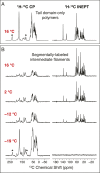
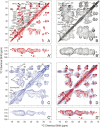
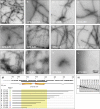
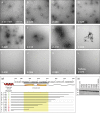
The coiled-coil domains of intermediate filament (IF) proteins are flanked by regions of low sequence complexity. Whereas IF coiled-coil domains assume dimeric and tetrameric conformations on their own, maturation of eight tetramers into cylindrical IFs is dependent on either "head" or "tail" domains of low sequence complexity. Here we confirm that the tail domain required for assembly of Drosophila Tm1-I/C IFs functions by forming labile cross-β interactions. These interactions are seen in polymers made from the tail domain alone, as well as in assembled IFs formed by the intact Tm1-I/C protein. The ability to visualize such interactions in situ within the context of a discrete cellular assembly lends support to the concept that equivalent interactions may be used in organizing other dynamic aspects of cell morphology.
Keywords: cross-beta polymerization; intermediate filaments; low-complexity proteins; solid-state NMR.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ephrussi A., Lehmann R., Induction of germ cell formation by oskar. Nature 358, 387–392 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Gavis E. R., Lehmann R., Translational regulation of nanos by RNA localization. Nature 369, 315–318 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Bardsley A., McDonald K., Boswell R. E., Distribution of tudor protein in the Drosophila embryo suggests separation of functions based on site of localization. Development 119, 207–219 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Hay B., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Localization of vasa, a component of Drosophila polar granules, in maternal-effect mutants that alter embryonic anteroposterior polarity. Development 109, 425–433 (1990). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

