Locus-specific analysis of DNA methylation patterns in cloned and in vitro fertilized porcine embryos
- PMID: 32908081
- PMCID: PMC7768172
- DOI: 10.1262/jrd.2019-076
Locus-specific analysis of DNA methylation patterns in cloned and in vitro fertilized porcine embryos
Abstract
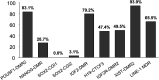
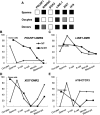
Porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) is currently inefficient, as 1-3.95% of reconstructed embryos survive to term; inadequate or erroneous epigenetic reprogramming of the specialized donor somatic nucleus could be a primary reason. Therefore, a locus-specific analysis of DNA methylation dynamics in embryogenesis and the DNA methylation status of gametes and donor cells used for SCNT were conducted in the following developmentally important gene loci: POU5F1, NANOG, SOX2, H19, IGF2, IGF2R, XIST; and the retrotransposon LINE-1. There were significant epigenetic differences between the gametes and the somatic donor cells. Three gamete-specific differentially methylated regions (DMRs) in POU5F1, XIST, and LINE-1 were identified. A delayed demethylation process at POU5F1 and LINE-1 loci occurred after three successive cleavages, compared to the in vitro fertilized (IVF) embryos. Although cloned embryos could undergo de-methylation and re-methylation dynamics at the DMRs of imprinted genes (H19, IGF2R, and XIST), the re-methylation process was compromised, unlike in fertilized embryos. LINE-1 loci are widely dispersed across the whole genome, and LINE-1 DMR might be a potential porcine nuclear reprogramming epi-marker. Data from observations in our present and previous studies, and two published articles were pooled to produce a schematic diagram of locus-specific, DNA methylation dynamics of cloned and IVF embryos during porcine early embryogenesis. This also indicated aberrant DNA methylation reprogramming events, including inadequate DNA demethylation and insufficient re-methylation in cloned embryos. Further research should focus on mechanisms underlying demethylation during the early cleavage of embryos and de novo DNA methylation at the blastocyst stage.
Keywords: Cloned embryos; DNA methylation; Donor cells; In vitro fertilized embryos; Porcine.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Oxamflatin treatment enhances cloned porcine embryo development and nuclear reprogramming.Cell Reprogram. 2015 Feb;17(1):28-40. doi: 10.1089/cell.2014.0075. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Cell Reprogram. 2015. PMID: 25548976 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of DNMT1 and HDAC inhibitors on gene-specific methylation reprogramming during porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer.PLoS One. 2013 May 31;8(5):e64705. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064705. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23741375 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant DNA methylation reprogramming in bovine SCNT preimplantation embryos.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 26;6:30345. doi: 10.1038/srep30345. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27456302 Free PMC article.
-
Germline-derived DNA methylation and early embryo epigenetic reprogramming: The selected survival of imprints.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;67:128-38. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.04.014. Epub 2015 May 9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25966912 Review.
-
Epigenetic modification is central to genome reprogramming in somatic cell nuclear transfer.Stem Cells. 2006 Apr;24(4):805-14. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2005-0350. Epub 2005 Nov 10. Stem Cells. 2006. PMID: 16282443 Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis of melatonin treatment and porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryo development.Anim Reprod. 2021 Nov 4;18(3):e20210031. doi: 10.1590/1984-3143-AR2021-0031. eCollection 2021. Anim Reprod. 2021. PMID: 34840610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole-genome methylation analysis reveals epigenetic variation between wild-type and nontransgenic cloned, ASMT transgenic cloned dairy goats generated by the somatic cell nuclear transfer.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2022 Nov 25;13(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s40104-022-00764-6. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36434676 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation regulates RNA m6A modification through transcription factor SP1 during the development of porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos.Cell Prolif. 2024 May;57(5):e13581. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13581. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 38095020 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of α-Ketoglutarate levels by Myc affects metabolism and demethylation in porcine early embryos.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Nov 26;12:1507102. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1507102. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39659520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- West FD, Uhl EW, Liu Y, Stowe H, Lu Y, Yu P, Gallegos-Cardenas A, Pratt SL, Stice SL. Brief report: chimeric pigs produced from induced pluripotent stem cells demonstrate germline transmission and no evidence of tumor formation in young pigs. Stem Cells 2011; 29: 1640–1643. - PubMed
-
- Groenen MA, Archibald AL, Uenishi H, Tuggle CK, Takeuchi Y, Rothschild MF, Rogel-Gaillard C, Park C, Milan D, Megens HJ, Li S, Larkin DM, Kim H, Frantz LA, Caccamo M, Ahn H, Aken BL, Anselmo A, Anthon C, Auvil L, Badaoui B, Beattie CW, Bendixen C, Berman D, Blecha F, Blomberg J, Bolund L, Bosse M, Botti S, Bujie Z, Bystrom M, Capitanu B, Carvalho-Silva D, Chardon P, Chen C, Cheng R, Choi SH, Chow W, Clark RC, Clee C, Crooijmans RP, Dawson HD, Dehais P, De Sapio F, Dibbits B, Drou N, Du ZQ, Eversole K, Fadista J, Fairley S, Faraut T, Faulkner GJ, Fowler KE, Fredholm M, Fritz E, Gilbert JG, Giuffra E, Gorodkin J, Griffin DK, Harrow JL, Hayward A, Howe K, Hu ZL, Humphray SJ, Hunt T, Hornshøj H, Jeon JT, Jern P, Jones M, Jurka J, Kanamori H, Kapetanovic R, Kim J, Kim JH, Kim KW, Kim TH, Larson G, Lee K, Lee KT, Leggett R, Lewin HA, Li Y, Liu W, Loveland JE, Lu Y, Lunney JK, Ma J, Madsen O, Mann K, Matthews L, McLaren S, Morozumi T, Murtaugh MP, Narayan J, Nguyen DT, Ni P, Oh SJ, Onteru S, Panitz F, Park EW, Park HS, Pascal G, Paudel Y, Perez-Enciso M, Ramirez-Gonzalez R, Reecy JM, Rodriguez-Zas S, Rohrer GA, Rund L, Sang Y, Schachtschneider K, Schraiber JG, Schwartz J, Scobie L, Scott C, Searle S, Servin B, Southey BR, Sperber G, Stadler P, Sweedler JV, Tafer H, Thomsen B, Wali R, Wang J, Wang J, White S, Xu X, Yerle M, Zhang G, Zhang J, Zhang J, Zhao S, Rogers J, Churcher C, Schook LB. Analyses of pig genomes provide insight into porcine demography and evolution. Nature 2012; 491: 393–398. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kurome M, Geistlinger L, Kessler B, Zakhartchenko V, Klymiuk N, Wuensch A, Richter A, Baehr A, Kraehe K, Burkhardt K, Flisikowski K, Flisikowska T, Merkl C, Landmann M, Durkovic M, Tschukes A, Kraner S, Schindelhauer D, Petri T, Kind A, Nagashima H, Schnieke A, Zimmer R, Wolf E. Factors influencing the efficiency of generating genetically engineered pigs by nuclear transfer: multi-factorial analysis of a large data set. BMC Biotechnol 2013; 13: 43. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bendixen E, Danielsen M, Larsen K, Bendixen C. Advances in porcine genomics and proteomics—a toolbox for developing the pig as a model organism for molecular biomedical research. Brief Funct Genomics 2010; 9: 208–219. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

