The influence of different sample preparation on mechanical properties of human iliotibial tract
- PMID: 32908171
- PMCID: PMC7481782
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-71790-5
The influence of different sample preparation on mechanical properties of human iliotibial tract
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: The influence of different sample preparation on mechanical properties of human iliotibial tract.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 25;11(1):2673. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81980-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33495496 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Author Correction: The influence of different sample preparation on mechanical properties of human iliotibial tract.Sci Rep. 2021 May 11;11(1):10404. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89952-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33976345 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
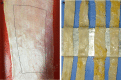
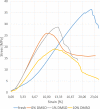
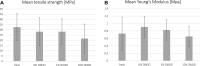
In the run-up to biomechanical testing, fresh human tissue samples are often frozen in order to inhibit initial decomposition processes and to achieve a temporal independence of tissue acquisition from biomechanical testing. The aim of this study was to compare the mechanical properties of fresh tissue samples of the human iliotibial tract (IT) to fresh-frozen samples taken from the same IT and those modified with different concentrations of Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) prior to freezing. All samples were partial plastinated and destructive tensile tests were conducted with a uniaxial tensile test setup. A plastination technique already established in the laboratory was modified to improve the clamping behaviour of the samples. Material failure was caused by a gradual rupture of the load-bearing collagen fibre bundles. Contrary to our expectations, no significant difference was found between the tensile strength of fresh and fresh frozen specimens. The addition of 1 wt% DMSO did not increase the tensile strength compared to fresh-frozen samples; an addition of 10 wt% DMSO even resulted in a decrease. Based on our findings, the use of simple fresh-frozen specimens to determine the tensile strength is viable; however fresh specimens should be used to generate a complete property profile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

