2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) dysregulates hepatic one carbon metabolism during the progression of steatosis to steatohepatitis with fibrosis in mice
- PMID: 32908189
- PMCID: PMC7481292
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-71795-0
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) dysregulates hepatic one carbon metabolism during the progression of steatosis to steatohepatitis with fibrosis in mice
Abstract
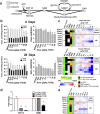
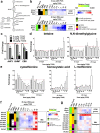
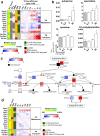
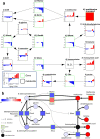
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), a persistent environmental contaminant, induces steatosis that can progress to steatohepatitis with fibrosis, pathologies that parallel stages in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Coincidently, one carbon metabolism (OCM) gene expression and metabolites are often altered during NAFLD progression. In this study, the time- and dose-dependent effects of TCDD were examined on hepatic OCM in mice. Despite AhR ChIP-seq enrichment at 2 h, OCM gene expression was not changed within 72 h following a bolus dose of TCDD. Dose-dependent repression of methionine adenosyltransferase 1A (Mat1a), adenosylhomocysteinase (Achy) and betaine-homocysteine S-methyltransferase (Bhmt) mRNA and protein levels following repeated treatments were greater at 28 days compared to 8 days. Accordingly, levels of methionine, betaine, and homocysteic acid were dose-dependently increased, while S-adenosylmethionine, S-adenosylhomocysteine, and cystathionine exhibited non-monotonic dose-dependent responses consistent with regulation by OCM intermediates and repression of glycine N-methyltransferase (Gnmt). However, the dose-dependent effects on SAM-dependent metabolism of polyamines and creatine could not be directly attributed to alterations in SAM levels. Collectively, these results demonstrate persistent AhR activation disrupts hepatic OCM metabolism at the transcript, protein and metabolite levels within context of TCDD-elicited progression of steatosis to steatohepatitis with fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dysregulated Hepatic Methionine Metabolism Drives Homocysteine Elevation in Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 31;10(8):e0136822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136822. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26322888 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-Dependent Metabolic Reprogramming and Differential Gene Expression in TCDD-Elicited Hepatic Fibrosis.Toxicol Sci. 2016 Dec;154(2):253-266. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfw163. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Toxicol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27562557 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) Activation by 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin (TCDD) Dose-Dependently Shifts the Gut Microbiome Consistent with the Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 18;22(22):12431. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212431. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830313 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic effects of methionine adenosyltransferases deregulation as determinants of liver cancer progression and prognosis.J Hepatol. 2013 Oct;59(4):830-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.031. Epub 2013 May 7. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23665184 Review.
-
Alcoholic liver disease and methionine metabolism.Semin Liver Dis. 2009 May;29(2):155-65. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1214371. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Semin Liver Dis. 2009. PMID: 19387915 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of Epigenetic Mechanisms into Non-Genotoxic Carcinogenicity Hazard Assessment: Focus on DNA Methylation and Histone Modifications.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 11;22(20):10969. doi: 10.3390/ijms222010969. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) elicited dose-dependent shifts in the murine urinary metabolome associated with hepatic AHR-mediated differential gene expression.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 25:2024.10.22.619714. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.22.619714. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39484576 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Cell-specific AHR-driven differential gene expression in the mouse liver cell following acute TCDD exposure.BMC Genomics. 2024 Aug 28;25(1):809. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10730-3. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39198768 Free PMC article.
-
The Association between Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Advanced Fibrosis with Serological Vitamin B12 Markers: Results from the NHANES 1999-2004.Nutrients. 2022 Mar 14;14(6):1224. doi: 10.3390/nu14061224. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35334881 Free PMC article.
-
TCDD attenuates EAE through induction of FasL on B cells and inhibition of IgG production.Toxicology. 2021 Jan 30;448:152646. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2020.152646. Epub 2020 Nov 28. Toxicology. 2021. PMID: 33253778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friso S, Udali S, De Santis D, Choi SW. One-carbon metabolism and epigenetics. Mol. Aspects Med. 2017;54:28–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

