Genetic Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci for Egg Production and Egg Quality Traits in Chickens: a Review
- PMID: 32908402
- PMCID: PMC7477176
- DOI: 10.2141/jpsa.0160121
Genetic Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci for Egg Production and Egg Quality Traits in Chickens: a Review
Abstract
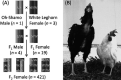
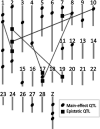
Chickens display a wide spectrum of phenotypic variations in quantitative traits such as egg-related traits. Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis is a statistical method used to understand the relationship between phenotypic (trait measurements) and genotypic data (molecular markers). We have performed QTL analyses for egg-related traits using an original resource population based on the Japanese Large Game (Oh-Shamo) and the White Leghorn breeds of chickens. In this article, we summarize the results of our extensive QTL analyses for 11 and 66 traits for egg production and egg quality, respectively. We reveal that at least 30 QTL regions on 17 different chromosomes affect phenotypic variation in egg-related traits. Each locus had an age-specific effect on traits, and a variety in effects was also apparent, such as additive, dominance, and epistatic-interaction effects. Although genome-wide association study (GWAS) is suitable for gene-level resolution mapping of GWAS loci with additive effects, QTL mapping studies enable us to comprehensively understand genetic control, such as chromosomal regions, genetic contribution to phenotypic variance, mode of inheritance, and age-specificity of both common and rare alleles. QTL analyses also describe the relationship between genotypes and phenotypes in experimental populations. Accumulation of QTL information, including GWAS loci, is also useful for studies of population genomics approached without phenotypic data in order to validate the identified genomic signatures of positive selection. The combination of QTL studies and next-generation sequencing techniques with uncharacterized genetic resources will enhance current understanding of the relationship between genotypes and phenotypes in livestock animals.
Keywords: chickens; egg production trait; egg quality trait; epistasis; genotype-phenotype relationship; quantitative trait loci.
2017, Japan Poultry Science Association.
Figures


References
-
- Abasht B, Sandford E, Arango J, Settar P, Fulton JE, O'Sullivan NP, Hassen A, Habier D, Fernando RL, Dekkers JCM, Lamont SJ. Extent and consistency of linkage disequilibrium and identification of DNA markers for production and egg quality traits in commercial layer chicken populations. BMC Genomics, 10: S2 2009. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Broman KW, Wu H, Sen S, Churchill GA. R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics, 19: 889-890. 2003. - PubMed
-
- Broman KW, Sen S. A guide to QTL mapping with R/qtl. Springer, New York: 2009.

