Sexual and Reproductive Health Services Utilization and Associated Factors among College Students at West Arsi Zone in Oromia Region, Ethiopia
- PMID: 32908460
- PMCID: PMC7468662
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3408789
Sexual and Reproductive Health Services Utilization and Associated Factors among College Students at West Arsi Zone in Oromia Region, Ethiopia
Abstract
Background: Young people are challenged with sexual and reproductive health (SRH) problems due to limited access to services and information. It contributes a high burden of sexually transmitted disease, unsafe abortion, and premature mortality, especially in low-income countries like Ethiopia. Hence, this study aimed at assessing the SRH service utilization and associated factors among college students at West Arsi Zone in Oromia region, Ethiopia.
Methods: Institutional-based cross-sectional study was conducted among 519 randomly selected college students from January 01, 2019, up to April 30, 2019. Data were collected through self-administered pretested questionnaires. Data entry and analysis for descriptive and logistic regression models were performed by using SPSS (version 23). The result was declared as statistically significant at p < 0.05.
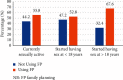
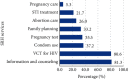
Results: The utilization of at least one SRH service in the last twelve months was seen in 304 (58.6%) students. Mainly information and counseling (81.3%), voluntary testing and counseling for HIV (80.6%), condom service (37.2%), pregnancy test (35.5%), family planning services (33.2%), and abortion care services (26.0%) were most frequently utilized. The students' aged between 20 and 24 years [AOR = 2.05, 95% CI: 1.38-3.06], female students [AOR = 1.92, 95% CI: 1.30-2.82], those not living with family [AOR = 1.54, 95% CI: 1.05-2.26], those who discussed about SRH with family/friends [AOR = 1.92, 95% CI: 1.31-2.82], and those who participated in school clubs [AOR = 1.75, 95% CI: 1.19, 2.58] more frequently used SRH service compared with their counterparts.
Conclusions: The utilization of SRH services was low when compared with other studies and needs improvements to tackle RH-related problems. It requires pertinent health education and the SRH club at higher educational institutions is crucial.
Copyright © 2020 Demelash Wachamo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations Development of Economic and Social Association. Youth Population Trends and Sustainable Development. New York City, NY, USA: United Nations Development of Economic and Social Association; 2015.
-
- Bremner J., Frost A., Haub C., Mather M., Ringheim K., Zuehlke E. World population highlights: key findings from PRB’s 2010 world population data sheet. Population Bulletin. 2010;65(2):1–12.
-
- Motuma A. Youth-friendly health services utilization and factors in Harar, Ethiopia. Harar Bulletin of Health Sciences Extracts. 2012;4
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

