Mindfulness Training Enhances Endurance Performance and Executive Functions in Athletes: An Event-Related Potential Study
- PMID: 32908483
- PMCID: PMC7474752
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8213710
Mindfulness Training Enhances Endurance Performance and Executive Functions in Athletes: An Event-Related Potential Study
Abstract
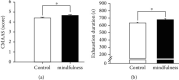
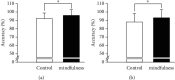
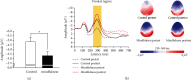
Mindfulness interventions have been linked to improved sport performance and executive functions; however, few studies have explored the effects of mindfulness on sport performance and executive functions simultaneously. This study sought to examine whether a mindfulness training program would affect both the endurance performance and executive functions of athletes. In addition, event-related potentials (ERPs) associated with the Stroop task were assessed to investigate the potential electrophysiological activation associated with the mindfulness training. Applying a quasiexperimental design, forty-six university athletes were recruited and assigned into a five-week mindfulness training program or a waiting list control group. For each participant, the mindfulness level, endurance performance assessed by a graded exercise test, executive functions assessed via Stroop task, and N2 component of ERPs were measured prior to and following the 5-week intervention. After adjusting for the preintervention scores as a covariate, it was found that the postintervention mindfulness level, exhaustion time, and Stroop task accuracy scores, regardless of task condition, of the mindfulness group were higher than those of the control group. The mindfulness group also exhibited a smaller N2 amplitude than the control group. These results suggest that the five-week mindfulness program can enhance the mindfulness level, endurance performance, and multiple cognitive functions, including executive functions, of university athletes. Mindfulness training may also reduce conflict monitoring in neural processes.
Copyright © 2020 Jui-Ti Nien et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Athletes with meditation experience counteract the detrimental effect of mental fatigue on endurance performance and neurocognitive functions.J Sports Sci. 2024 Jul;42(14):1355-1366. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2024.2391651. Epub 2024 Aug 19. J Sports Sci. 2024. PMID: 39158157 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of functional overreaching on executive functions.Int J Sports Med. 2010 Sep;31(9):617-23. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1255029. Epub 2010 Jun 11. Int J Sports Med. 2010. PMID: 20544582
-
Sequential conflict resolution under multiple concurrent conflicts: An ERP study.Neuroimage. 2019 Mar;188:411-418. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.12.031. Epub 2018 Dec 15. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 30562575
-
A review on the electroencephalography markers of Stroop executive control processes.Brain Cogn. 2020 Dec;146:105637. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2020.105637. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Brain Cogn. 2020. PMID: 33217721 Review.
-
Effects of Mindfulness Practice on Performance-Relevant Parameters and Performance Outcomes in Sports: A Meta-Analytical Review.Sports Med. 2017 Nov;47(11):2309-2321. doi: 10.1007/s40279-017-0752-9. Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 28664327 Review.
Cited by
-
The relationship between mindfulness and athletes' mental skills may be explained by emotion regulation and self-regulation.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024 Mar 19;16(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13102-024-00863-z. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38504372 Free PMC article.
-
A new multidimensional group intervention for cognitive and psychosocial functioning for older adults: Background, content, and process evaluation.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 20;10:1161060. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1161060. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37153102 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Aerobic Fitness Dynamics in Post-COVID-19 Athletes: Implications in the Return-to-Play Performance.Sports (Basel). 2025 Feb 5;13(2):40. doi: 10.3390/sports13020040. Sports (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39997971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Mindfulness for Performance Programme on Actual Performance in Ecological Sport Context: Two Studies in Basketball and Table Tennis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 10;19(19):12950. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912950. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36232246 Free PMC article.
-
Effortful and effortless training of executive functions improve brain multiple demand system activities differently: an activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 14;17:1243409. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1243409. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38033550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kabat-Zinn J. Mindfulness-based interventions in context: past, present, and future. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice. 2006;10(2):144–156. doi: 10.1093/clipsy.bpg016. - DOI
-
- Cillessen L., Johannsen M., Speckens A. E. M., Zachariae R. Mindfulness-based interventions for psychological and physical health outcomes in cancer patients and survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Psychooncology. 2019;28(12):2257–2269. doi: 10.1002/pon.5214. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

