Network Pharmacology-Based Approach to Revealing Biological Mechanisms of Qingkailing Injection against IschemicStroke: Focusing on Blood-Brain Barrier
- PMID: 32908557
- PMCID: PMC7474352
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2914579
Network Pharmacology-Based Approach to Revealing Biological Mechanisms of Qingkailing Injection against IschemicStroke: Focusing on Blood-Brain Barrier
Abstract
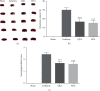
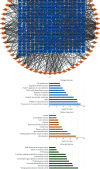
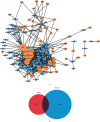
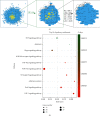
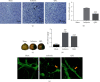
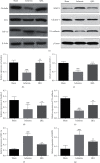
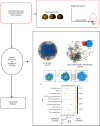
Ischemic stroke is the most common type of cerebrovascular accident worldwide. It causes long-term disability and death. Qingkailing (QKL) injection is a traditional Chinese patent medicine which has been clinically applied in the treatment of ischemic stroke for nearly thirty years. In the present study, network pharmacology combined with experimentation was used to elucidate the mechanisms of QKL. ADME screening and target prediction identified 62 active compounds and 275 targets for QKL. Topological screening of the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was used to build a core PPI network consisting of 408 nodes and 17,830 edges. KEGG enrichment indicated that the main signaling pathway implicated in ischemic stroke involved hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). Experimentation showed that QKL alleviated neurological deficits, brain infraction, blood-brain barrier (BBB) leakage, and tight junction degeneration in a mouse ischemic stroke model. Two-photon laser scanning microscopy was used to evaluate BBB permeability and cerebral microvessel structure in living mice. HIF-1α, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), and tight junction proteins such as occludin, zonula occludins-1 (ZO-1), claudin-5, and VE-Cadherin were measured by western blotting. QKL upregulated ZO-1 and downregulated HIF-1α and MMP-9. QKL has a multiapproach, multitarget, and synergistic effect against ischemic stroke.
Copyright © 2020 Shuang Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An Integrative Pharmacology-Based Analysis of Refined Qingkailing Injection Against Cerebral Ischemic Stroke: A Novel Combination of Baicalin, Geniposide, Cholic Acid, and Hyodeoxycholic Acid.Front Pharmacol. 2020 May 8;11:519. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00519. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32457601 Free PMC article.
-
Protective mechanism of Erigeron breviscapus injection on blood-brain barrier injury induced by cerebral ischemia in rats.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 16;11(1):18451. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97908-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34531475 Free PMC article.
-
Qingkailing injection ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and modulates the AMPK/NLRP3 Inflammasome Signalling pathway.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Nov 20;19(1):320. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2703-5. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31747940 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology assessment of Qingkailing injection treatment of cholestatic hepatitis.J Tradit Chin Med. 2021 Feb;41(1):167-180. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20201208.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 33522210 Review.
-
From static to dynamic: live observation of the support system after ischemic stroke by two photon-excited fluorescence laser-scanning microscopy.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Oct;18(10):2093-2107. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.369099. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 37056116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Network pharmacology analysis reveals neuroprotective effects of the Qin-Zhi-Zhu-Dan Formula in Alzheimer's disease.Front Neurosci. 2022 Oct 20;16:943400. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.943400. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36340795 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Chinese Herbal Medicine for Cerebral Ischemic Reperfusion Injury.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 17;12:688596. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.688596. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35111041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Anti-inflammatory Properties of Corydalis rhizoma for Co-Treatment of Neuropathic Pain and Major Depressive Disorder: Network Pharmacology with Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Approaches.Curr Top Med Chem. 2025 Apr 11:10.2174/0115680266354824250327072413. doi: 10.2174/0115680266354824250327072413. Online ahead of print. Curr Top Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40231535 Free PMC article.
-
Interpreting the Mechanism of Active Ingredients in Polygonati Rhizoma in Treating Depression by Combining Systemic Pharmacology and In Vitro Experiments.Nutrients. 2024 Apr 14;16(8):1167. doi: 10.3390/nu16081167. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38674858 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanism Study of Common Flavonoids on Antiglioma Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jan 31;2022:2198722. doi: 10.1155/2022/2198722. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35140796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamin E. J. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation. 2018;137(12) - PubMed
-
- Murray C. J., Vos T., Lozano R., Naghavi M. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet (London, England) 2012;380(9859):2197–2223. - PubMed
-
- SrSS Group. The national institute of neurological disorders and stroke rt-PA stroke study group tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. New England Journal of Medicine. 1996;333:1581–1588. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

