Network Pharmacology to Uncover the Biological Basis of Spleen Qi Deficiency Syndrome and Herbal Treatment
- PMID: 32908629
- PMCID: PMC7474375
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2974268
Network Pharmacology to Uncover the Biological Basis of Spleen Qi Deficiency Syndrome and Herbal Treatment
Abstract
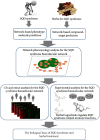
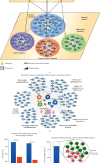
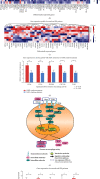
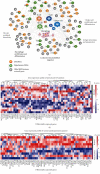
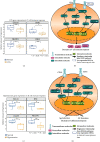
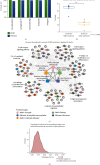
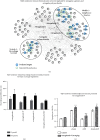
Spleen qi deficiency (SQD) syndrome is one of the basic traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) syndromes related to various diseases including chronic inflammation and hypertension and guides the use of many herbal formulae. However, the biological basis of SQD syndrome has not been clearly elucidated due to the lack of appropriate methodologies. Here, we propose a network pharmacology strategy integrating computational, clinical, and experimental investigation to study the biological basis of SQD syndrome. From computational aspects, we used a powerful disease gene prediction algorithm to predict the SQD syndrome biomolecular network which is significantly enriched in biological functions including immune regulation, oxidative stress, and lipid metabolism. From clinical aspects, SQD syndrome is involved in both the local and holistic disorders, that is, the digestive diseases and the whole body's dysfunctions. We, respectively, investigate SQD syndrome-related digestive diseases including chronic gastritis and irritable bowel syndrome and the whole body's dysfunctions such as chronic fatigue syndrome and hypertension. We found innate immune and oxidative stress modules of SQD syndrome biomolecular network dysfunction in chronic gastritis patients and irritable bowel syndrome patients. Lymphocyte modules were downregulated in chronic fatigue syndrome patients and hypertension patients. From experimental aspects, network pharmacology analysis suggested that targets of Radix Astragali and other four herbs commonly used for SQD syndrome are significantly enriched in the SQD syndrome biomolecular network. Experiments further validated that Radix Astragali ingredients promoted immune modules such as macrophage proliferation and lymphocyte proliferation. These findings indicate that the biological basis of SQD syndrome is closely related to insufficient immune response including decreased macrophage activity and reduced lymphocyte proliferation. This study not only demonstrates the potential biological basis of SQD syndrome but also provides a novel strategy for exploring relevant molecular mechanisms of disease-syndrome-herb from the network pharmacology perspective.
Copyright © 2020 Xin Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative study on the gastrointestinal- and immune- regulation functions of Hedysari Radix Paeparata Cum Melle and Astragali Radix Praeparata cum Melle in rats with spleen-qi deficiency, based on fuzzy matter-element analysis.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):1237-1254. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2086990. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35763552 Free PMC article.
-
Identifications of metabolic differences between Hedysari Radix Praeparata Cum Melle and Astragali Radix Praeparata Cum Melle for spleen-qi deficiency rats: A comparative study.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023 Nov 30;236:115689. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115689. Epub 2023 Aug 29. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023. PMID: 37677887
-
Biological network comparison identifies a novel synergistic mechanism of Ginseng Radix-Astragali Radix herb pair in cancer-related fatigue.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Oct 28;333:118447. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118447. Epub 2024 Jun 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38885914
-
TCM network pharmacology: A new trend towards combining computational, experimental and clinical approaches.Chin J Nat Med. 2021 Jan;19(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(21)60001-8. Chin J Nat Med. 2021. PMID: 33516447 Review.
-
[Network target: a starting point for traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2011 Aug;36(15):2017-20. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22066431 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Multi-omics approaches for deciphering the complexity of traditional Chinese medicine syndromes in stroke: A systematic review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 6;13:980650. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.980650. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36147315 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Plant-Derived Natural Compounds in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis: A Review of the Treatment Potential and Development Strategy.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 28;12:639651. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.639651. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34262447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determination of the synergistic anti-influenza effect of Huangqin Su tablet and Oseltamivir and investigation of mechanism of the tablet based on gut microbiota and network pharmacology.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Feb 4;23(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03858-4. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 36739385 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Mechanism of Üstikuddus Sherbiti in Ischemic Cerebrovascular Diseases: Based on Network Pharmacology.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Apr 8;2022:5581864. doi: 10.1155/2022/5581864. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35432563 Free PMC article.
-
Xiahuo Pingwei San attenuated intestinal inflammation in dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis mice through inhibiting the receptor for advanced glycation end-products signaling pathway.J Tradit Chin Med. 2025 Apr;45(2):311-325. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.006. J Tradit Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40151118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang S., Hu L., Li R. Expert consensus on tcm diagnosis and treatment of spleen deficiency syndrome. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2017;58(17):1525–1530.
-
- Lin J., Hu J., Liu B. Research on conceptual framework of pro scale in spleen-qi deficiency syndrome. Tianjin Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2013;30(5):277–281.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

