Computer-Aided System for the Detection of Multicategory Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Radiographs
- PMID: 32908660
- PMCID: PMC7463336
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/9205082
Computer-Aided System for the Detection of Multicategory Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Radiographs
Abstract
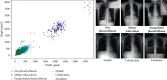
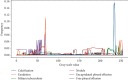
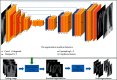
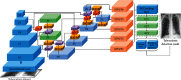
The early screening and diagnosis of tuberculosis plays an important role in the control and treatment of tuberculosis infections. In this paper, an integrated computer-aided system based on deep learning is proposed for the detection of multiple categories of tuberculosis lesions in chest radiographs. In this system, the fully convolutional neural network method is used to segment the lung area from the entire chest radiograph for pulmonary tuberculosis detection. Different from the previous analysis of the whole chest radiograph, we focus on the specific tuberculosis lesion areas for the analysis and propose the first multicategory tuberculosis lesion detection method. In it, a learning scalable pyramid structure is introduced into the Faster Region-based Convolutional Network (Faster RCNN), which effectively improves the detection of small-area lesions, mines indistinguishable samples during the training process, and uses reinforcement learning to reduce the detection of false-positive lesions. To compare our method with the current tuberculosis detection system, we propose a classification rule for whole chest X-rays using a multicategory tuberculosis lesion detection model and achieve good performance on two public datasets (Montgomery: AUC = 0.977 and accuracy = 0.926; Shenzhen: AUC = 0.941 and accuracy = 0.902). Our proposed computer-aided system is superior to current systems that can be used to assist radiologists in diagnoses and public health providers in screening for tuberculosis in areas where tuberculosis is endemic.
Copyright © 2020 Yilin Xie et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Machine and Deep Learning for Tuberculosis Detection on Chest X-Rays: Systematic Literature Review.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Jul 3;25:e43154. doi: 10.2196/43154. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37399055 Free PMC article.
-
Automated detection of moderate and large pneumothorax on frontal chest X-rays using deep convolutional neural networks: A retrospective study.PLoS Med. 2018 Nov 20;15(11):e1002697. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002697. eCollection 2018 Nov. PLoS Med. 2018. PMID: 30457991 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal matrix size of chest radiographs for computer-aided detection on lung nodule or mass with deep learning.Eur Radiol. 2020 Sep;30(9):4943-4951. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06892-9. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32350657
-
Automatic tuberculosis screening using chest radiographs.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2014 Feb;33(2):233-45. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2013.2284099. Epub 2013 Oct 1. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24108713
-
Convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection or diagnosis in medical image analysis: An overview.Math Biosci Eng. 2019 Jul 15;16(6):6536-6561. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2019326. Math Biosci Eng. 2019. PMID: 31698575 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine and Deep Learning for Tuberculosis Detection on Chest X-Rays: Systematic Literature Review.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Jul 3;25:e43154. doi: 10.2196/43154. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37399055 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary Pulmonary Tuberculosis Identification Via pseudo-Zernike Moment and Deep Stacked Sparse Autoencoder.J Grid Comput. 2022;20(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s10723-021-09596-6. Epub 2021 Dec 16. J Grid Comput. 2022. PMID: 34931118 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning-Based Classification and Semantic Segmentation of Lung Tuberculosis Lesions in Chest X-ray Images.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Apr 30;14(9):952. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14090952. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38732366 Free PMC article.
-
COFE-Net: An ensemble strategy for Computer-Aided Detection for COVID-19.Measurement (Lond). 2022 Jan;187:110289. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110289. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Measurement (Lond). 2022. PMID: 34663998 Free PMC article.
-
A voting-based ensemble deep learning method focusing on image augmentation and preprocessing variations for tuberculosis detection.Neural Comput Appl. 2021;33(22):15541-15555. doi: 10.1007/s00521-021-06177-2. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Neural Comput Appl. 2021. PMID: 34121816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2019. Global Tuberculosis Report 2019.
-
- World Health Organization. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2016. Radiography in Tuberculosis Detection.
-
- Pai D. B. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2012. Tuberculosis: Diagnostic Technology Landscape. Unitaid secretariat.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

