COVID-19 in a Patient with Accidental Drug-Induced Neutropenia
- PMID: 32908840
- PMCID: PMC7473687
- DOI: 10.12890/2020_001848
COVID-19 in a Patient with Accidental Drug-Induced Neutropenia
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) presents with a wide range of illness severity, from asymptomatic disease to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Immunosuppression is considered a risk factor for severe COVID-19, but there are only few reports on disease progression in immunocompromised patients.
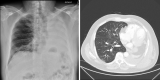
Case summary: We report the case of a 50-year-old patient with acute COVID-19 pneumonia, who had iatrogenic, clinically relevant bone marrow suppression due to accidental overdose with hydroxyurea, and decreased lung capacity due to a left-sided pneumonectomy 6 months earlier. Symptomatic treatment with oxygen supplementation and pulmonary physical therapy was initiated, and hydroxyurea was discontinued. Over 14 days, the patient's blood counts slowly recovered, and his clinical condition gradually improved, such that supplemental oxygen was no longer necessary and he could be discharged.
Discussion: A gradual increase in neutrophil and lymphocyte counts may be preferable to dampen a potentially detrimental immunological response triggered by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Whether patients with severe COVID-19 benefit from immunosuppressive therapy should be further evaluated.
Learning points: Acute respiratory distress syndrome is a serious complication in COVID-19 and appears to be triggered by a proinflammatory cytokine storm.Immunosuppression may avoid an immune hyper-response triggered by SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: COVID-19; clinical course; neutropenia; pneumectomy.
© EFIM 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The Authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Horby P, Lim WS, Emberson J, Mafham M, Bell J, Linsell L, et al. Effect of dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19—preliminary report. medRxiv. Jun 22, 2020. (preprint). Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.06.22.20137273v1.full.pdf. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous