Identification of Biomarkers to Construct a Competing Endogenous RNA Network and Establishment of a Genomic-Clinicopathologic Nomogram to Predict Survival for Children with Rhabdoid Tumors of the Kidney
- PMID: 32908900
- PMCID: PMC7474367
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5843874
Identification of Biomarkers to Construct a Competing Endogenous RNA Network and Establishment of a Genomic-Clinicopathologic Nomogram to Predict Survival for Children with Rhabdoid Tumors of the Kidney
Abstract
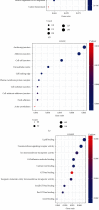
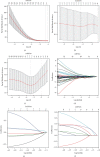
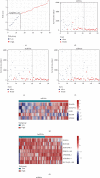
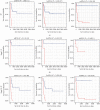
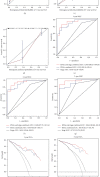
Rhabdoid tumor of the kidney (RTK) is a rare and severely malignant tumor occurring in infancy and early childhood, with the overall outcomes remain poor. Neither gene regulatory networks nor biomarkers to predict the prognostic outcomes have been elucidated in RTK. In this study, RNA sequencing data were obtained to identify differentially expressed messenger RNAs (mRNAs), long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), and microRNAs (miRNAs) between RTK samples and normal samples. A total of 4217 mRNAs, 284 lncRNAs, and 286 miRNAs were screened out. Of those, 103 mRNAs, 80 lncRNAs, and 45 miRNAs were identified for a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) regulatory network, in which three significant modules were identified. A protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed, and the hub-gene cluster consisted of four core genes (EXOSC2, PAK1IP1, WDR43, and POLR1D) was selected. Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses were also performed to analyze the functional characteristics of differentially expressed mRNAs. Subsequently, among 211 mRNAs, 8 lncRNAs, and 12 miRNAs associated with overall survival (OS) obtained by univariate Cox analysis, 5 mRNAs, 7 lncRNAs, and 7 miRNAs were identified and the risk score formulas were constructed correspondingly using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) Cox regression model analysis. The log-rank tests and Kaplan-Meier analyses were performed to confirm the predictive value of the risk scores for OS in RTK patients. A genomic-clinicopathologic nomogram integrating the stage and risk scores based on RNAs was established and demonstrated high predictive accuracy and clinical value, which was validated through calibration curves, time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses, and decision curve analysis (DCA). In conclusion, this study not only provided potential insights into the mechanisms underlying RTK, but also presented a practicable tool for predicting the prognosis in children with RTK.
Copyright © 2020 Xiaoqing Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of Potential Biomarkers of Prognosis-Related Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) in Pediatric Rhabdoid Tumor of the Kidney Based on ceRNA Networks.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Dec 17;26:e927725. doi: 10.12659/MSM.927725. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 33328429 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of RNA Expression Profiles in Thyroid Cancer to Construct a Competing Endogenous RNA (ceRNA) Network of mRNAs, Long Noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), and microRNAs (miRNAs).Med Sci Monit. 2019 Feb 12;25:1140-1154. doi: 10.12659/MSM.912450. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 30745559 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of lncRNA-Associated ceRNA Network Reveals Potential lncRNA Biomarkers in Human Colon Adenocarcinoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(5):1778-1791. doi: 10.1159/000493623. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30231249
-
Reconstruction and Analysis of the Differentially Expressed IncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(6):539-549. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2019028740. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 32422009 Review.
-
Identification of a competing endogenous RNA network associated with prognosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Jun 11;20:231. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01243-6. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32536819 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune-Related LncRNAs as Prognostic Factors for Pediatric Rhabdoid Tumor of the Kidney.Dis Markers. 2022 Jun 15;2022:4752184. doi: 10.1155/2022/4752184. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35756490 Free PMC article.
-
A POLR1D-regulating single-nucleotide polymorphism as a predictive marker candidate for platinum-based chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancers.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 13;17:17588359251355079. doi: 10.1177/17588359251355079. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40661991 Free PMC article.
-
From simple factors to artificial intelligence: evolution of prognosis prediction in childhood cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Nov 21;78:102902. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102902. eCollection 2024 Dec. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39640942 Free PMC article.
-
NRP1 knockdown inhibits the invasion and migration of rhabdoid tumor of the kidney cells.Pediatr Surg Int. 2024 Aug 12;40(1):221. doi: 10.1007/s00383-024-05808-8. Pediatr Surg Int. 2024. PMID: 39133317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reinhard H., Reinert J., Beier R., et al. Rhabdoid tumors in children: prognostic factors in 70 patients diagnosed in Germany. Oncology Reports. 2008;19(3):819–823. - PubMed
-
- Van den Heuvel-Eibrink M. M., van Tinteren H., Rehorst H., et al. Malignant rhabdoid tumours of the kidney (MRTKs), registered on recent SIOP protocols from 1993 to 2005: a report of the SIOP renal tumour study group. Pediatric Blood & Cancer. 2011;56(5):733–737. doi: 10.1002/pbc.22922. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tekautz T. M., Fuller C. E., Blaney S., et al. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors (ATRT): improved survival in children 3 years of age and older with radiation therapy and high-dose alkylator-based chemotherapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23(7):1491–1499. doi: 10.1200/jco.2005.05.187. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

