DNA Primase Subunit 1 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Clinical Implication
- PMID: 32908930
- PMCID: PMC7463366
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/9689312
DNA Primase Subunit 1 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Clinical Implication
Abstract
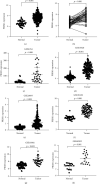
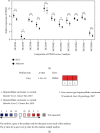
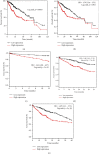
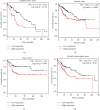
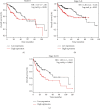
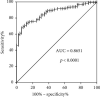
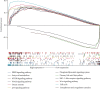
DNA Primase Subunit 1 (PRIM1) is crucial for cancer development and progression. However, there remains a lack of comprehension concerning the clinical implication of PRIM1 in HCC. Here, aberrant expression of PRIM1 was identified in HCC according to available databases. The prognostic value of PRIM1 in patients presenting with HCC was further assessed based on TCGA data. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was subsequently conducted to investigate the potential function of PRIM1. Additionally, the correlations between tumor-infiltrating immune cells (TIICs) and PRIM1 expression were evaluated. The data from TCGA, GEO, ONCOMINE, and HCCDB databases illustrated that PRIM1 was overexpressed in HCC tissues, compared to normal liver tissues (all p < 0.05). Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that high PRIM1 expression in HCC was closely correlated with worse overall survival (p < 0.05). The univariate and multivariate analyses illustrated that PRIM1 expression was an independent novel prognostic indicator in HCC. Additionally, the area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve for PRIM1 reached 0.8651, indicating the diagnostic significance of PRIM1 in patients with HCC. GSEA showed that PRIM1 overexpression was significantly enriched in several tumor-related signaling pathways. Besides, TIIC analysis clarified the association between PRIM1 expression and TIICs in HCC. The findings disclose that PRIM1 profoundly implicated in promoting tumorigenesis might work as a desirable biomarker for HCC.
Copyright © 2020 Yipeng Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

