A phase 2a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, add-on clinical trial of ebselen (SPI-1005) as a novel treatment for mania or hypomania
- PMID: 32909076
- PMCID: PMC7683468
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-020-05654-1
A phase 2a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, add-on clinical trial of ebselen (SPI-1005) as a novel treatment for mania or hypomania
Abstract
Rationale: Lithium is an effective prophylactic and anti-manic treatment in bipolar disorder; however, its use is declining through perceived poor tolerance and toxicity. Lithium inhibits inositol monophosphatase (IMPase), a probable key therapeutic mechanism. The anti-inflammatory drug, ebselen, also inhibits IMPase and appears well-tolerated and safe.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy of adjunctive ebselen in mania using the Young Mania Rating Scale (YMRS) (primary outcome) and the Altman Self-Rating Mania (ASRM) Scale and Clinical Global Impression-Severity Scale (CGI-S) among the secondary outcomes.
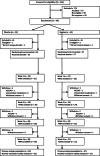
Methods: Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial conducted between October 2017 and June 2019, at Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust. Pharmacy-controlled randomisation was computer-generated, with full allocation concealment. In/outpatients (n = 68) aged 18-70, experiencing mania or hypomania, were assigned to 3 weeks ebselen (600 mg bd) (n = 33) or placebo (n = 35). Participants received usual clinical care and psychotropic medication.
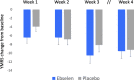
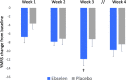
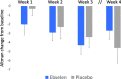
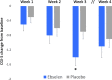
Results: Ebselen was numerically, but not statistically, superior to placebo in lowering scores on the YMRS (adjusted mean difference and 95% confidence interval, - 1.71 (- 5.34 to 1.91), p = 0.35) and ASRM (- 1.36 (- 3.75 to 1.17), p = 0.29). However, scores on the CGI-S were significantly lower at week 3 in ebselen-treated participants (adjusted mean difference, - 0.58 (- 1.14 to - 0.03), p = 0.04). A post hoc analysis excluding patients taking concomitant valproate treatment magnified the difference between ebselen and placebo on the YMRS. Adverse events were comparable between groups, and mild.
Conclusions: Ebselen merits further investigation where concomitant psychotropic medication is better controlled and participants taking valproate are excluded. If effective, ebselen's superior tolerance and safety could make it a useful alternative to lithium.
Trial registration: Trial Registry: www.clinicaltrials.gov , Identifier: NCT03013400.
Keywords: Add-on; Bipolar; Ebselen; Lithium mimetic; Mania; Randomised clinical trial; YMRS.
Conflict of interest statement
NS holds a method-of-use patent (WO/2012/107735) for ebselen in the treatment of bipolar disorder. ALS, CW, AAH, BRG, MS, OM and PJC declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

