Limiting homologous recombination at stalled replication forks is essential for cell viability: DNA2 to the rescue
- PMID: 32909097
- PMCID: PMC7599155
- DOI: 10.1007/s00294-020-01106-7
Limiting homologous recombination at stalled replication forks is essential for cell viability: DNA2 to the rescue
Abstract
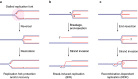
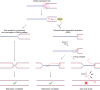
The disease-associated nuclease-helicase DNA2 has been implicated in DNA end-resection during DNA double-strand break repair, Okazaki fragment processing, and the recovery of stalled DNA replication forks (RFs). Its role in Okazaki fragment processing has been proposed to explain why DNA2 is indispensable for cell survival across organisms. Unexpectedly, we found that DNA2 has an essential role in suppressing homologous recombination (HR)-dependent replication restart at stalled RFs. In the absence of DNA2-mediated RF recovery, excessive HR-restart of stalled RFs results in toxic levels of abortive recombination intermediates that lead to DNA damage-checkpoint activation and terminal cell-cycle arrest. While HR proteins protect and restart stalled RFs to promote faithful genome replication, these findings show how HR-dependent replication restart is actively constrained by DNA2 to ensure cell survival. These new insights disambiguate the effects of DNA2 dysfunction on cell survival, and provide a framework to rationalize the association of DNA2 with cancer and the primordial dwarfism disorder Seckel syndrome based on its role in RF recovery.
Keywords: Chromosome stability; DNA replication fork; DNA replication stress; DNA2 nuclease–helicase; Homologous recombination; Seckel syndrome.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

