Modified method for effective primary vascular smooth muscle progenitor cell culture from peripheral blood
- PMID: 32909140
- PMCID: PMC7547929
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-020-00419-2
Modified method for effective primary vascular smooth muscle progenitor cell culture from peripheral blood
Abstract
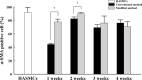
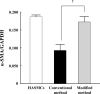
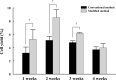
In previous studies, vascular smooth muscle progenitor cells (vSMPCs) isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were cultured using medium containing platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) for 4 weeks. However, this method requires long culture periods of up to 4 weeks and yields low cell counts. Therefore, we proposed the modified method to improve the cell yield and purity and to reduce the cell culture period. PBMCs were isolated from human peripheral blood and cultured by the conventional method using medium containing PDGF-BB alone or the modified method using medium containing PDGF-BB, basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), and insulin-transferrin-selenium ITS for 4 weeks. The purity of vSMPCs was analyzed for the expression of a- smooth muscle actin (SMA) by flow cytometry and significantly higher in the modified method than conventional methods at the 1st and 2nd weeks. Also, mRNA expression of a-SMA by real-time PCR was significantly higher in the modified method than conventional method at the 2 weeks. The yield of vSMPCs by trypan blue exclusion assay was significantly higher in the modified method than conventional method at the 1st, 2nd and 3rd weeks. The primary culture using the modified method with PDGF-BB, bFGF, and ITS not only improved cell purity and yield, but also shortened the culture period, compared to the conventional culture method for vSMPCs. The modified method will be a time-saving and useful tool in various studies related to vascular pathology.
Keywords: Cell culture; PBMCs; PDGF-BB; Peripheral blood; VSMPCs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest..
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Effects of endostatin pretreatment on fibrosis of human skin fibroblasts and the mechanisms].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2017 Nov 20;33(11):694-698. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2017.11.007. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29166712 Chinese.
-
[PDGF-BB initiates vascular smooth muscle-like phenotype differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro].Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007 Jul;23(4):335-9. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 17926862 Chinese.
-
Endothelial progenitor cells derived from CD34+ cells form cooperative vascular networks.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010;26(4-5):679-88. doi: 10.1159/000322335. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010. PMID: 21063105
-
Fibroblast growth factor, epidermal growth factor, insulin-like growth factors, and platelet-derived growth factor-BB stimulate proliferation of clonally derived porcine myogenic satellite cells.J Cell Physiol. 1993 Nov;157(2):326-32. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041570216. J Cell Physiol. 1993. PMID: 8227164
-
[Platelet derived growth factor-BB regulates phenotype transformation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells via SIRT3 affecting glycolytic pathway].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2019 Dec 24;47(12):993-999. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2019.12.009. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31877596 Chinese.
References
-
- Chua KH, Aminuddin BS, Fuzina NH, Ruszymah BH (2005) Insulin-transferrin-selenium prevent human chondrocyte dedifferentiation and promote the formation of high quality tissue engineered human hyaline cartilage Eur Cell Mater 9:58-67; discussion 67 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

