Cellular retinol binding protein 1 transfection reduces proliferation and AKT-related gene expression in H460 non-small lung cancer cells
- PMID: 32909215
- PMCID: PMC7561531
- DOI: 10.1007/s11033-020-05744-5
Cellular retinol binding protein 1 transfection reduces proliferation and AKT-related gene expression in H460 non-small lung cancer cells
Abstract
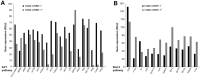
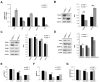
In recent years, new treatments with novel action mechanisms have been explored for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Retinoids promote cancer cell differentiation and death and their trafficking and action is mediated from specific cytoplasmic and nuclear receptors, respectively. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of Cellular retinol binding protein-1 (CRBP-1) transfection in H460 human NSCLC cell line, normally not expressing CRBP-1. H460 cells were transfected by using a vector pTargeT Mammalian expression system carrying the whole sequence of CRBP-1 gene. For proliferation and apoptosis studies, cells were treated with different concentrations of all-trans Retinoic Acid (atRA) and retinol. AKT-related gene expression was analyzed by using western blot and Signosis array and results analysed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) or by t-student test. CRBP-1+ showed reduced proliferation and viability in basal condition and after atRA treatment when compared to empty-transfected H460 cells. Reduced proliferation in CRBP-1+ H460 cells associated to the down-regulation of pAKT/pERK/pEGFR-related genes. In particular, gene array documented the down-regulation of AKT and Stat-3-related genes, including M-Tor, Akt1, Akt2, Akt3, Foxo1, p27, Jun. Restoration of CRBP-1 expression in H460 cells reduced proliferation and viability in both basal condition and after atRA treatment, likely by down-regulating AKT-related gene level. Further studies are needed to better clarify how those CRBP-1-related intracellular pathways contribute to counteract NSCLC progression in order to suggest a potential tool to improve efficacy of retinoid anti lung cancer adjuvant therapy.
Keywords: AKT pathway; CRBP-1; Non-small cell lung cancer; Retinoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CRBP-1 expression in ovarian cancer: a potential therapeutic target.Anticancer Res. 2014 Jul;34(7):3303-12. Anticancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24982334
-
Vitamin A, cancer treatment and prevention: the new role of cellular retinol binding proteins.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:624627. doi: 10.1155/2015/624627. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25879031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRBP suppresses breast cancer cell survival and anchorage-independent growth.Oncogene. 2001 Nov 1;20(50):7413-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204749. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11704871
-
Silencing the FOLR2 Gene Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Increases Apoptosis in the NCI-H1650 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Line via Inhibition of AKT/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR)/Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase 1 (S6K1) Signaling.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Nov 11;24:8064-8073. doi: 10.12659/MSM.911384. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30415267 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular retinoid binding-proteins, CRBP, CRABP, FABP5: Effects on retinoid metabolism, function and related diseases.Pharmacol Ther. 2017 May;173:19-33. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28132904 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophages depletion alleviates lung injury by modulating AKT3/GXP4 following ventilator associated pneumonia.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 5;14:1260584. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1260584. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. Retraction in: Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 25;15:1513341. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1513341. PMID: 37731502 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Establishment of a Preoperative Laboratory Panel to identify Lymph Node Metastasis in Superficial Esophageal Cancer.J Cancer. 2022 Apr 11;13(7):2238-2245. doi: 10.7150/jca.71114. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35517400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Quintero Barceinas RS, Garcia-Regalado A, Arechaga-Ocampo E, Villegas-Sepulveda N, Gonzalez-De la Rosa CH. All-trans retinoic acid induces proliferation, survival, and migration in A549 lung cancer cells by activating the ERK signaling pathway through a transcription-independent mechanism. BioMed Res Int. 2015 doi: 10.1155/2015/404368. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karamouzis MV, Ardavanis A, Alexopoulos A, et al. Multiple cutaneous acral metastases in a woman with breast adenocarcinoma treated with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin: incidental or aetiological association? Eur J Cancer Care. 2005;14(3):267–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2354.2005.00573.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

