Hepatocyte growth factor intervention to reduce myocardial injury and improve cardiac function on diabetic myocardial infarction rats
- PMID: 32909423
- PMCID: PMC7445436
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2020.3142
Hepatocyte growth factor intervention to reduce myocardial injury and improve cardiac function on diabetic myocardial infarction rats
Abstract
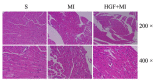
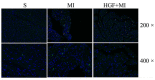
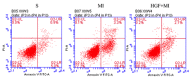
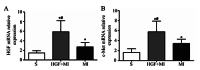
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is recognized to be a severe threat to people's health conditions and life quality. The accumulation of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) in ischemic myocardium has been observed in both processes of experimental ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) and permanent coronary artery occlusion. The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of HGF on myocardial cell apoptosis, ventricular remodeling and cardiac function after myocardial infarction (MI) in diabetic rats, and to explore whether the effect is mediated by HGF/c-Met signaling pathway. MI significantly increases LVWI and RVWI and myocardial apoptotic index, and up-regulates the expression of HGF and c-Met at mRNA and protein levels in MI control group. The LVWI and RVWI, and myocardial apoptosis were reduced by treatment with HGF, which also increased the myocardial cell viability and the expression of HGF and c-Met. In summary, HGF significantly attenuates myocardial apoptosis and improves cardiac function after AMI in diabetic rats by further enhancing the activation of HGF/c-Met pathway.
Figures
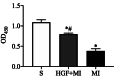
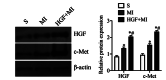
Similar articles
-
Myocardial protection from ischemia/reperfusion injury by endogenous and exogenous HGF.J Clin Invest. 2000 Dec;106(12):1511-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI10226. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 11120758 Free PMC article.
-
A potential cardioprotective role of hepatocyte growth factor in myocardial infarction in rats.Cardiovasc Res. 2001 Jul;51(1):41-50. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(01)00272-3. Cardiovasc Res. 2001. PMID: 11399246
-
The role of cytoprotective cytokines in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury.J Surg Res. 2008 Aug;148(2):164-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.08.005. Epub 2007 Aug 31. J Surg Res. 2008. PMID: 18067924
-
The therapeutic potential of hepatocyte growth factor for myocardial infarction and heart failure.Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(20):2525-33. doi: 10.2174/1381612043383863. Curr Pharm Des. 2004. PMID: 15320761 Review.
-
Targeting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt through hepatocyte growth factor for cardioprotection.J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2013 Apr;14(4):249-53. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0b013e3283542017. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2013. PMID: 22609872 Review.
Cited by
-
Twenty years of histochemistry in the third millennium, browsing the scientific literature.Eur J Histochem. 2020 Dec 29;64(4):3213. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2020.3213. Eur J Histochem. 2020. PMID: 33478199 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic angiogenesis and tissue revascularization in ischemic vascular disease.J Biol Eng. 2023 Feb 16;17(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13036-023-00330-2. J Biol Eng. 2023. PMID: 36797776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Efficacy of Transplanting Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sheets in the Treatment of Myocardial Infarction in Mice.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 3;11(8):2187. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082187. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Kolte D, Khera S, Aronow HD, Abbott JD, Bhatt DL, et al. Diabetes mellitus and cardiogenic shock complicating acute myocardial infarction. Am J Med 2018;131:778-86. - PubMed
-
- Sardella G, Mancone M, Stio RE, Cavallo E, Di Roma A, Colantonio R, et al. Prasugrel or ticagrelor in ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction patients with diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2017;136:602-4. - PubMed
-
- Otsuki Y, Nakamura Y, Harada S, Yamamoto Y, Ogino K, Morikawa K, et al. Adipose stem cell sheets improved cardiac function in the rat myocardial infarction, but did not alter cardiac contractile responses to beta-adrenergic stimulation. Biomed Res 2015;36:11-9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

