Beyond ecstasy: Alternative entactogens to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine with potential applications in psychotherapy
- PMID: 32909493
- PMCID: PMC8155739
- DOI: 10.1177/0269881120920420
Beyond ecstasy: Alternative entactogens to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine with potential applications in psychotherapy
Abstract
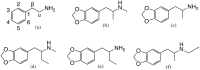
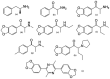
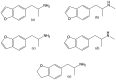
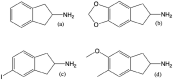
The last two decades have seen a revival of interest in the entactogen 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine (MDMA) as an adjunct to psychotherapy, particularly for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder. While clinical results are highly promising, and MDMA is expected to be approved as a treatment in the near future, it is currently the only compound in its class of action that is being actively investigated as a medicine. This lack of alternatives to MDMA may prove detrimental to patients who do not respond well to the particular mechanism of action of MDMA or whose treatment calls for a modification of MDMA's effects. For instance, patients with existing cardiovascular conditions or with a prolonged history of stimulant drug use may not fit into the current model of MDMA-assisted psychotherapy, and could benefit from alternative drugs. This review examines the existing literature on a host of entactogenic drugs, which may prove to be useful alternatives in the future, paying particularly close attention to any neurotoxic risks, neuropharmacological mechanism of action and entactogenic commonalities with MDMA. The substances examined derive from the 1,3-benzodioxole, cathinone, benzofuran, aminoindane, indole and amphetamine classes. Several compounds from these classes are identified as potential alternatives to MDMA.
Keywords: Entactogen; MDMA; PTSD; empathogen; psychotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The entactogen 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA; ecstasy) as a treatment aid in psychotherapy and its safety concerns.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Aug;98(8):2409-2427. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03765-8. Epub 2024 May 14. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38743292 Review.
-
[MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD].Laeknabladid. 2024 May;110(5):254-261. doi: 10.17992/lbl.2024.05.793. Laeknabladid. 2024. PMID: 38713560 Review. Icelandic.
-
Methylenedioxymethamphetamine is a connectogen with empathogenic, entactogenic, and still further connective properties: It is time to reconcile "the great entactogen-empathogen debate".J Psychopharmacol. 2024 Aug;38(8):685-689. doi: 10.1177/02698811241265352. Epub 2024 Jul 28. J Psychopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39068642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MDMA-Assisted Therapy for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: Regulatory Challenges and a Path Forward.CNS Drugs. 2025 Apr;39(4):339-343. doi: 10.1007/s40263-025-01162-y. Epub 2025 Feb 15. CNS Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39955464
-
A comparison of MDMA-assisted psychotherapy to non-assisted psychotherapy in treatment-resistant PTSD: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Psychopharmacol. 2021 May;35(5):501-511. doi: 10.1177/0269881120965915. Epub 2020 Dec 20. J Psychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33345689
Cited by
-
AddictedChem: A Data-Driven Integrated Platform for New Psychoactive Substance Identification.Molecules. 2022 Jun 19;27(12):3931. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123931. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35745053 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine on Conditioned Fear Extinction and Retention in a Crossover Study in Healthy Subjects.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 13;13:906639. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.906639. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35910354 Free PMC article.
-
Balancing Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of MDMA and Novel MDXX Analogues as Novel Treatments for Autism Spectrum Disorder.Psychedelic Med (New Rochelle). 2023 Sep 13;1(3):166-185. doi: 10.1089/psymed.2023.0023. eCollection 2023 Sep. Psychedelic Med (New Rochelle). 2023. PMID: 40046567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A proposed mechanism for the MDMA-mediated extinction of traumatic memories in PTSD patients treated with MDMA-assisted therapy.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Oct 12;13:991753. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.991753. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36311515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Benzofuran Derivatives Induce Monoamine Release and Substitute for the Discriminative Stimulus Effects of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024 Sep 18;391(1):22-29. doi: 10.1124/jpet.123.001837. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024. PMID: 38272669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ask AL, Fagervall I, Huang RB, et al.. (1989) Release of 3H-5-hydroxytryptamine by amiflamine and related phenylalkylamines from rat occipital cortex slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 339: 684–689. - PubMed
-
- Baggott MJ, Coyle JR, Siegrist JD, et al.. (2016) Effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine on socioemotional feelings, authenticity, and autobiographical disclosure in healthy volunteers in a controlled setting. J Psychopharmacol 30: 378–387. - PubMed
-
- Baggott MJ, Garrison KJ, Coyle JR, et al., (2019) Effects of the psychedelic amphetamine MDA (3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine) in healthy volunteers. J Psychoactive Drugs 51: 108–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

