Pharmacodynamic analysis of apremilast in Japanese patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: Results from a phase 2b randomized trial
- PMID: 32909643
- PMCID: PMC7821327
- DOI: 10.1111/1346-8138.15596
Pharmacodynamic analysis of apremilast in Japanese patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: Results from a phase 2b randomized trial
Abstract
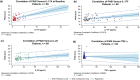
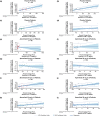
We evaluated the pharmacodynamic effects of apremilast in 69 patients who were included in biomarker subanalyses of a phase 2b study that demonstrated the long-term safety and efficacy of apremilast in Japanese adults with moderate to severe psoriasis. The association between cytokine levels and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) improvement was evaluated using linear regression and Spearman's rank correlation coefficient analysis. At baseline, median plasma levels of interleukin (IL)-17A, IL-17F and IL-22 were elevated versus reference values for healthy individuals, whereas tumor necrosis factor-α levels were close to normal. With apremilast 30 mg b.i.d., there were significant associations between percentage change in PASI score and percentage change in IL-17A, IL-17F and IL-22 levels at week 16. Findings demonstrate that the efficacy of apremilast in psoriasis is associated with inhibition of key cytokines involved in the pathology of psoriasis.
Keywords: apremilast; biomarker analysis; cytokines; pharmacodynamics; psoriasis.
© 2020 The Authors. The Journal of Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Dermatological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
S. I. received research funds, consultancy fees and speaker fees from Celgene, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, LEO Pharma, Maruho and Novartis. Y. O. received grants from Eisai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Maruho and Mitsubishi‐Tanabe. P. S. and R. P. were employed by Bristol‐Myers Squibb, and Celgene at the time of study conduct. M. O. received grants and personal fees from AbbVie, Eisai, Mitsubishi‐Tanabe and Novartis. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Schafer PH, Parton A, Capone L et al Apremilast is a selective PDE4 inhibitor with regulatory effects on innate immunity. Cell Signal 2014; 26(9): 2016–2029. - PubMed
-
- Gottlieb AB, Matheson RT, Menter A et al Efficacy, tolerability, and pharmacodynamics of apremilast in recalcitrant plaque psoriasis: a phase II open‐label study. J Drugs Dermatol 2013; 12(8): 888–897. - PubMed
-
- Garcet S, Nograles K, Correa da Rosa J, Schafer PH, Krueger JG. Synergistic cytokine effects as apremilast response predictors in patients with psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2018; 142(3): 1010–1013.e1016. - PubMed
-
- Ohtsuki M, Okubo Y, Komine M et al Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in the treatment of Japanese patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: Efficacy, safety and tolerability results from a phase 2b randomized controlled trial. J Dermatol 2017; 44(8): 873–884. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Papp K, Reich K, Leonardi CL et al Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: results of a phase III, randomized, controlled trial (Efficacy and Safety Trial Evaluating the Effects of Apremilast in Psoriasis [ESTEEM 1]). J Am Acad Dermatol 2015; 73(1): 37–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

