Detection of specific IgE against linear epitopes from Gal d 1 has additional value in diagnosing hen's egg allergy in adults
- PMID: 32909666
- PMCID: PMC7756380
- DOI: 10.1111/cea.13730
Detection of specific IgE against linear epitopes from Gal d 1 has additional value in diagnosing hen's egg allergy in adults
Abstract
Background: Although hen's egg allergy is more prevalent in children, up to 0.6% of adults from different European countries suffer from a persistent or newly onset hen's egg allergy, making accurate diagnosis in adults necessary. However, sensitization to hen's egg extracts, components and linear epitopes is solely studied in children.
Methods: Hen's egg allergic (n = 16) and tolerant (n = 19) adults were selected by sensitization towards recombinant components rGal d 1 and/or 3. Sensitization profiles towards egg white and yolk extract and the native components Gal d 1, 2, 3 and 4 were respectively evaluated with the ImmunoCAP or the EUROLINE system. Characterization of linear epitopes was performed with a peptide microarray containing 15mer peptides representing the entire sequence of mature Gal d 1 and 3.
Results: Overall, sIgE titres against hen's egg extracts and single components overlapped largely between allergic and tolerant adults. Although the median sIgE/sIgG4 ratio to Gal d 1 was increased in allergic adults, the range was comparable between both groups. Clinically relevant sensitization to Gal d 1 was confirmed by sIgE-binding to the linear epitopes aa30-41, aa39-50 or aa84-95 in 6/13 allergic adults, mainly suffering from objective symptoms. In comparison, these epitopes were recognized by 1/15 tolerant patient. Only a few linear epitopes were detected for Gal d 3, suggesting a greater importance of conformational epitopes for the recognition of Gal d 3.
Conclusion and clinical relevance: Specific IgE-binding to linear epitopes of Gal d 1 is highly specific in identifying hen's egg allergic adults with objective symptoms.
Keywords: IgE; food allergy; hen; linear epitopes's egg.
© 2020 The Authors. Clinical & Experimental Allergy published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
E. Wierzba, U. Flügge and W. Suer are employees of EUROIMMUN AG, Lübeck, Germany. The research position of A. Ehlers is partially funded by EUROIMMUN AG, Lübeck, Germany. Other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


 , moderate
, moderate  and high
and high  . B, original WB showing sIgE‐binding to the recombinant components rGal d 1 and rGal d 3
. B, original WB showing sIgE‐binding to the recombinant components rGal d 1 and rGal d 3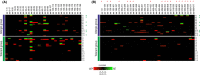
Similar articles
-
Ovomucoid (Gal d 1) specific IgE detected by microarray system predict tolerability to boiled hen's egg and an increased risk to progress to multiple environmental allergen sensitisation.Clin Exp Allergy. 2012 Mar;42(3):441-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2011.03915.x. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012. PMID: 22168465 Clinical Trial.
-
Molecular and immunological analysis of hen's egg yolk allergens with a focus on YGP42 (Gal d 6).Mol Immunol. 2016 Mar;71:152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2016.02.005. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Mol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26897338
-
Randomized placebo-controlled trial of hen's egg consumption for primary prevention in infants.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 May;139(5):1591-1599.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.06.045. Epub 2016 Aug 12. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27523961 Clinical Trial.
-
Molecular diagnosis of egg allergy: an update.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015;15(7):895-906. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2015.1041927. Epub 2015 May 15. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015. PMID: 25975845 Review.
-
Hen's Egg Allergy.Chem Immunol Allergy. 2015;101:124-30. doi: 10.1159/000375416. Epub 2015 May 21. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2015. PMID: 26022872 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Monoclonal IgE Antibodies-a Major Milestone in Allergy.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023 Jan;23(1):53-65. doi: 10.1007/s11882-022-01055-w. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023. PMID: 36459330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on In Vitro Diagnostic Tools and Treatments for Food Allergies.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 26;15(17):3744. doi: 10.3390/nu15173744. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37686776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into Isolation and Purification Strategies of Egg Allergens.Foods. 2025 May 29;14(11):1944. doi: 10.3390/foods14111944. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40509474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult onset egg allergy: a case report.Clin Mol Allergy. 2021 Oct 4;19(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12948-021-00156-7. Clin Mol Allergy. 2021. PMID: 34602090 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of peptides sequence and conformation contributed to potential allergenicity of main allergens in yogurts.Front Nutr. 2023 Jan 5;9:1038466. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1038466. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36687717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lyons S, Burney P, Ballmer‐Weber B, et al. Food allergy in adults: substantial variation in prevalence and causative foods across Europe. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7(6):1920‐1928. - PubMed
-
- Zuberbier T, Edenharter G, Worm M, et al. Prevalence of adverse reactions to food in Germany – a population study. Allergy. 2004;59(3):338‐345. - PubMed
-
- Soares‐Weiser K, Takwoingi Y, Panesar S, et al. The diagnosis of food allergy: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Allergy. 2014;69(1):76‐86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

