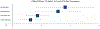Prescription Tranquilizer/Sedative Misuse Motives Across the US Population
- PMID: 32909984
- PMCID: PMC7937768
- DOI: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000736
Prescription Tranquilizer/Sedative Misuse Motives Across the US Population
Abstract
Objectives: Roughly 6.5 million US residents engaged in prescription tranquilizer/sedative (eg, benzodiazepines, Z-drugs) misuse in 2018, but tranquilizer/sedative misuse motives are understudied, with a need for nationally representative data and examinations of motives by age group. Our aims were to establish tranquilizer/sedative misuse motives and correlates of motives by age cohort, and whether motive-age cohort interactions existed by correlate.
Methods: Data were from the 2015 to 2018 US National Survey on Drug Use and Health, with 223,520 total respondents (51.5% female); 6580 noted past-year prescription tranquilizer/sedative misuse motives (2.4% overall, 50.3% female). Correlates included substance use (eg, opioid misuse), mental (eg, suicidal ideation) and physical health variables (e.g., inpatient hospitalization). Design-based, weighted cross-tabulations and logistic regression analyses were used, including analyses of age cohort-motive interactions for each correlate.
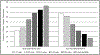
Results: Prescription tranquilizer/sedative misuse motives varied by age group, with the highest rates of self-treatment only motives (ie, sleep and/or relax) in those 65 and older (82.7%), and the highest rates of any recreational motives in adolescents (12-17 years; 67.5%). Any tranquilizer/sedative misuse was associated with elevated odds of substance use, mental health, and physical health correlates, but recreational misuse was associated with the highest odds. Age-based interactions suggested stronger relationships between tranquilizer/sedative misuse and mental health in adults 50 and older.
Conclusions: Any tranquilizer/sedative misuse signals a need for substance use and mental health screening, with intervention needs most acute in those with any recreational motives. Older adult tranquilizer/sedative misuse may be more driven by undertreated insomnia and anxiety/psychopathology than in younger groups.
Copyright © 2020 American Society of Addiction Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Barrett SP, Meisner JR, Stewart SH. What constitutes prescription drug misuse? Problems and pitfalls of current conceptualizations. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2008;1(3):255–262. - PubMed
-
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2018 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Detailed tables. Rockville, MD: Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration; 2019.
-
- 2019 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2019 Updated AGS Beers Criteria(R) for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(4):674–694. - PubMed
-
- Schepis TS. Age cohort differences in the nonmedical use of prescription zolpidem: findings from a nationally representative sample. Addict Behav. 2014;39(9):1311–1317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous