Analysis of the predictive factors for a critical illness of COVID-19 during treatment - relationship between serum zinc level and critical illness of COVID-19
- PMID: 32911042
- PMCID: PMC7476566
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.008
Analysis of the predictive factors for a critical illness of COVID-19 during treatment - relationship between serum zinc level and critical illness of COVID-19
Abstract
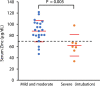
Objectives: Because most severely ill patients with COVID-19 in our hospital showed zinc deficiency, we aimed to examine the relationship between the patient's serum zinc level and severe cases of COVID-19.
Methods: Serum zinc <70 μg/dL was defined as the criterion for hypozincemia, and patients continuously with serum zinc <70 μg/dL were classified in the hypozincemia cohort. To evaluate whether hypozincemia could be a predictive factor for a critical illness of COVID-19, we performed a multivariate analysis by employing logistic regression analysis.
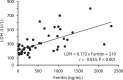
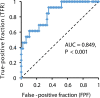
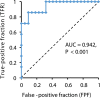
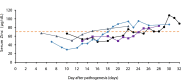
Results: Prolonged hypozincemia was found to be a risk factor for a severe case of COVID-19. In evaluating the relationship between the serum zinc level and severity of patients with COVID-19 by multivariate logistic regression analysis, critical illness can be predicted through the sensitivity and false specificity of a ROC curve with an error rate of 10.3% and AUC of 94.2% by only two factors: serum zinc value (P = 0.020) and LDH value (P = 0.026).
Conclusions: Proper management of the prediction results in this study can contribute to establishing and maintaining a safe medical system, taking the arrival of the second wave, and the spread of COVID-19 in the future into consideration.
Keywords: COVID-19; Critical illness; Japan; Logistic regression analysis; Predictive factors; Serum zinc.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Guy R.K., DiPaola R.S., Romanelli F., Dutch R.E. Rapid repurposing of drugs for COVID-19. Science. 2020;368(6493):829–830. - PubMed
-
- Higurashi K. Colorimetric reagent for zinc, ACCURAS AUTO Zn. Biomed Res Trace Elem. 2015;26(1):7–9.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

